0.官网
https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/trace/ftrace.html
1.ftrace是什么
ftrace是linux原生的一个trace工具,最早在2.6.27引入,跟踪能力强大, 可以调试和分析诸如延迟、代码路径、性能等。能很好帮助开发者知道内核正在干什么,从而更好的分析系统问题。
1.1 Ftrace 跟踪工具由性能分析器(profiler)和跟踪器(tracer)两部分组成:
性能分析器:用来提供统计和直方图数据(需要 CONFIG_ FUNCTION_PROFILER=y)
函数性能分析
直方图
跟踪器:提供跟踪事件的详情
函数跟踪(function)
点跟踪(tracepoint)
kprobe
uprobe
函数调用关系(function_graph)
hwlat 等
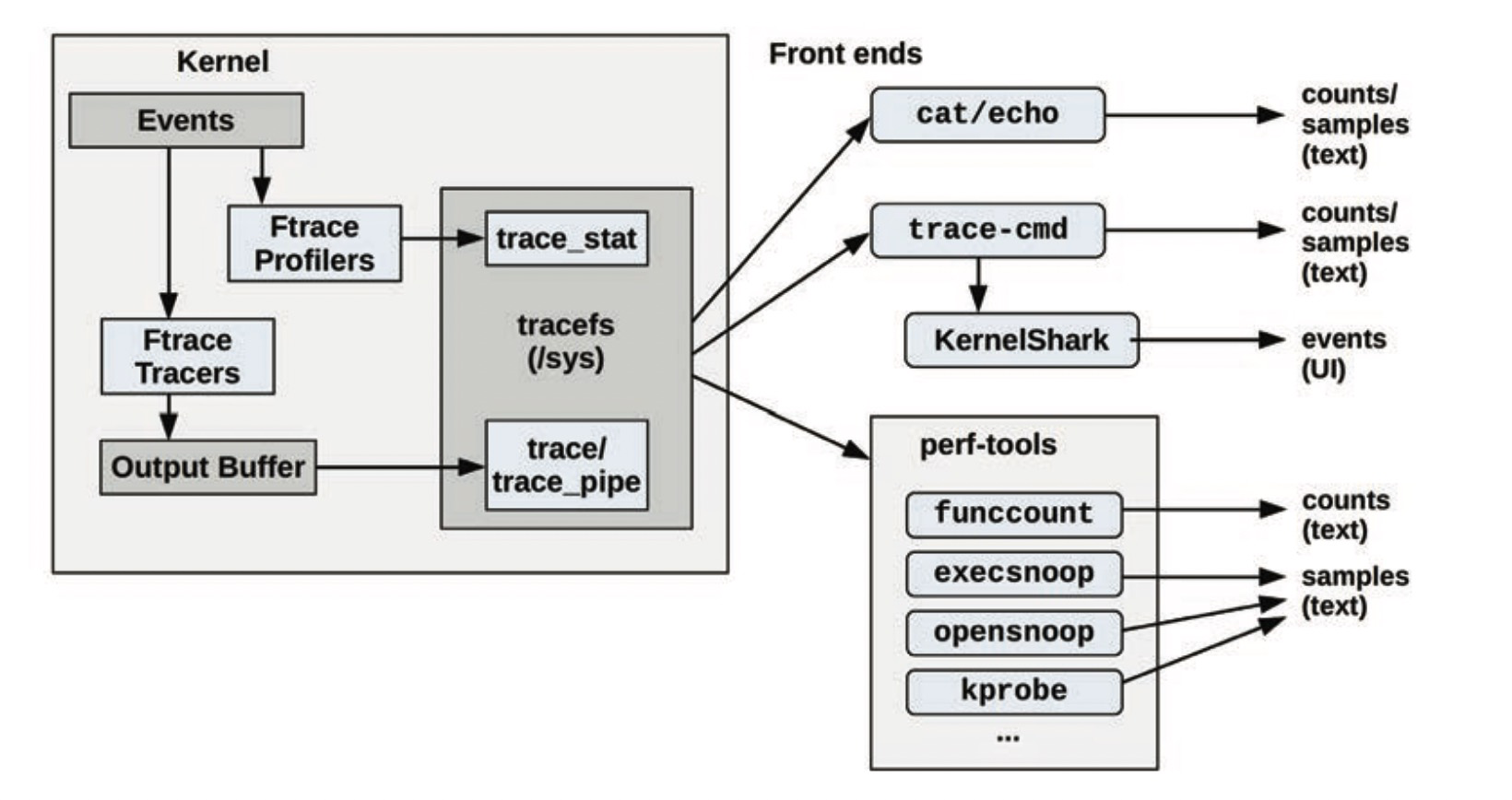
1.2 ftrace构成:
(1)提供函数钩子的基础设施;
(2)基于tracefs文件系统的trace框架;
除了原生操作,还有一些基于ftrace的前端工具,比如perf-tools和trace-cmd,关系图如下:
1.3Ftrace能做什么
Ftrace 可用来快速排查以下相关问题:
特定内核函数调用的频次 (function)
内核函数在被调用的过程中路径(调用栈) (function + stack)
内核函数调用的子函数流程(子调用栈)(function graph)
由于抢占导致的高延时路径等
https://www.daodaodao123.com/?p=695#step5
下面的实例操作,用之前搭建的arm64+linux环境来调试;
最简单的配置方法是编译内核时,将trace部分全部打开(开机频繁打印部分关掉);
2.使用方法
简单说,主要有三步:
设置 tracer 类型
设置 tracer 参数
使能 tracer进入 ftrace 工作目录:
cd /sys/kernel/debug/tracing查看系统支持的 tracer 类型:
cat available_tracers
hwlat blk function_graph wakeup_dl wakeup_rt wakeup irqsoff function nop案例1:Function trace
function默认会记录当前运行过程中的所有函数;
如果只想跟踪某个进程,可以使用set_ftrace_pid;
如果只想跟踪某个函数,可以使用set_ftrace_filter;
(0)关闭tracer
echo 0 > tracing_on清空打印
echo > trace(1)设置类型:
设current_tracer 类型为 function
echo function > current_tracer(2)设置参数:
如果开启动态配置选项,可以设置过滤函数,或指定跟踪函数
设置 trace 的过滤函数,即只跟踪blk_update_request
echo blk_update_request > set_ftrace_filter设置不跟踪指定函数;
echo > set_ftrace_filterecho blk_update_request > set_ftrace_notrace还可以用通配符"
'*match*':匹配所有包含match的函数;过滤所有以"hrtimer_"开头的函数echo 'hrtimer_*' >> set_ftrace_filter 还可以做基于模块的过滤:
例如,过滤 ext4 module 的 write* 函数:
控制范式:<function>:<command>:<parameter>echo 'write*:mod:ext4' > set_ftrace_filter感叹号用来移除某个函数,把多个组合过滤条件的某一个去掉:
echo '!ip_rcv' >> set_ftrace_filter遇到 __schedule_bug 函数后关闭 trace
echo '__schedule_bug:traceoff' > set_ftrace_filter(3)打开 trace 开关,开始 trace
echo 1 > tracing_on(4)提取 trace 结果
[root@myQEMU tracing]# cat trace
# tracer: function
#
# entries-in-buffer/entries-written: 6/6 #P:4
#
# _-----=> irqs-off
# / _----=> need-resched
# | / _---=> hardirq/softirq
# || / _--=> preempt-depth
# ||| / delay
# TASK-PID CPU# |||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION
# | | | |||| | |
<idle>-0 [001] ..s. 229.298724: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
<idle>-0 [001] ..s. 229.316890: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
<idle>-0 [001] ..s. 229.317916: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
<idle>-0 [001] ..s. 229.325217: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
<idle>-0 [001] d.s. 229.325280: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
sync-620 [001] ..s. 229.330068: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
[root@myQEMU tracing]# 从 trace 信息我们可以获取很多重要信息:
进程信息,TASK-PID
进程运行的 CPU
执行函数时的系统状态,包括中断,抢占等状态信息
执行函数的时间戳
function_graph使用方法和function类似,但可以更清晰的展示函数调用关系;
开启堆栈调用:可以跟踪函数被调用流程
cd /sys/kernel/debug/tracing
echo 0 > tracing_on
echo > trace
echo function > current_tracer
echo blk_update_request > set_ftrace_filter
echo 1 > options/func_stack_trace
echo 1 > options/irq-info
echo 1 > tracing_on
sleep 5
cat trace[root@myQEMU tracing]# cat /cpu.info
[root@myQEMU tracing]# cat trace
# tracer: function
#
# entries-in-buffer/entries-written: 18/18 #P:4
#
# _-----=> irqs-off
# / _----=> need-resched
# | / _---=> hardirq/softirq
# || / _--=> preempt-depth
# ||| / delay
# TASK-PID CPU# |||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION
# | | | |||| | |
cat-646 [000] ..s. 548.454890: blk_update_request <-blk_mq_end_request
cat-646 [000] ..s. 548.454915: <stack trace>
=> blk_update_request
=> blk_mq_end_request
=> virtblk_request_done
=> blk_complete_reqs
=> blk_done_softirq
=> __do_softirq
=> irq_exit
=> __handle_domain_irq
=> gic_handle_irq
=> el1_irq
=> get_page_from_freelist
=> __alloc_pages
=> page_cache_ra_unbounded
=> do_page_cache_ra
=> filemap_fault
=> ext4_filemap_fault
=> __do_fault
=> __handle_mm_fault
=> handle_mm_fault
=> do_page_fault
=> do_translation_fault
=> do_mem_abort
=> el0_ia
=> el0_sync_handler
=> el0_sync
案例2:function_graph
使用方法和function类似,但可以更清晰的展示函数调用关系;
开启堆栈调用,可以查看函数调用子函数堆栈
echo blk_update_request > set_graph_function
echo function_graph > current_tracer
echo 1 > options/func_stack_trace
echo 1 > tracing_on
cat /cpu.info 查看trace
[root@myQEMU home]# cat /tracing/trace
# tracer: function_graph
#
# CPU DURATION FUNCTION CALLS
# | | | | | | |
0) + 24.368 us | start_backtrace();
0) 4.336 us | start_backtrace();
0) | blk_update_request() {
0) 3.200 us | start_backtrace();
0) 3.152 us | start_backtrace();
0) + 68.576 us | }
0) | blk_update_request() {
0) 4.192 us | bio_advance();
0) | bio_endio() {
0) | submit_bio_wait_endio() {
0) | complete() {
0) | swake_up_locked() {
0) | swake_up_locked.part.0() {
0) | wake_up_process() {
0) | try_to_wake_up() {
0) | select_task_rq_fair() {
0) 3.808 us | available_idle_cpu();
0) 3.856 us | rcu_read_unlock_strict();
0) + 23.696 us | }
0) 3.968 us | ttwu_queue_wakelist();
0) 4.960 us | update_rq_clock.part.0();
0) | ttwu_do_activate.isra.0() {
0) | enqueue_task_fair() {
0) | update_curr() {
0) 4.064 us | __calc_delta();
0) 4.080 us | update_min_vruntime();
0) 4.192 us | rcu_read_unlock_strict();
0) + 31.056 us | }
0) 5.104 us | __update_load_avg_se();
0) | __update_load_avg_cfs_rq() {
0) 4.208 us | __accumulate_pelt_segments();
0) + 13.840 us | }
0) 4.544 us | __enqueue_entity();
0) + 77.328 us | }
0) | ttwu_do_wakeup.isra.0() {
0) | check_preempt_curr() {
0) | check_preempt_wakeup() {
0) 4.688 us | update_curr();
0) 4.640 us | wakeup_preempt_entity.isra.0();
0) + 23.616 us | }
0) + 32.976 us | }
0) + 50.688 us | }
0) ! 141.648 us | }
0) ! 198.064 us | }
0) ! 206.528 us | }
0) ! 215.072 us | }
0) ! 223.376 us | }
0) ! 232.320 us | }
0) ! 240.960 us | }
0) ! 250.400 us | }
0) ! 269.840 us | }
[root@myQEMU tracing]# 小技巧:用vim插件Documentation/trace/function-graph-fold.vim 打开,可以方便折叠函数方便查看,za(展开)/zc(折叠)
vim ft_graph.log -S Documentation/trace/function-graph-fold.vim
# tracer: function_graph
#
# CPU DURATION FUNCTION CALLS
# | | | | | | |
0) + 24.368 us | start_backtrace();
0) 4.336 us | start_backtrace();
+ 0) | blk_update_request() {----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 0) | blk_update_request() {
| 0) 4.192 us | bio_advance();
|- 0) | bio_endio() {
||- 0) | submit_bio_wait_endio() {
|||- 0) | complete() {
||||+ 0) | swake_up_locked() {-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|||| 0) ! 232.320 us | }
||| 0) ! 240.960 us | }
|| 0) ! 250.400 us | }
| 0) ! 269.840 us | }案例3:事件 trace
Ftrace的跟踪机制主要有两种:函数和tracepoint。
函数,案例1已经做了介绍;
tracepoint,可以理解为linux内核的占位符号,tracepoint可以输出开发者想要的参数,局部变量等。类似于C语言的#if DEBUG部分,不开启的话,不占用任何系统开销;
内核里常遇到以"trace_"开头的函数,比如CFS调度器里de update_curr()函数
static void update_curr(struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq)
{
...
update_min_vruntime(cfs_rq);
if (entity_is_task(curr)) {
struct task_struct *curtask = task_of(curr);
trace_sched_stat_runtime(curtask, delta_exec, curr->vruntime);
}
...
}
update_curr()函数使用了一个sched_stat_runtime的tracepoint, 可以在available_events看到;
查询系统支持的事件:
cat available_events |grep sched_stat_runtime
sched:sched_stat_runtime操作过程:
echo 0 > tracing_on
echo > trace
echo sched:sched_stat_runtime > set_event
echo 1 > tracing_on
#或者直接进入时间目录,等价操作:
cd /tracing/events/sched/sched_switch
echo 1 enable
cat /tracing/trace格式解析:
[root@myQEMU sched_stat_runtime]# cat format
name: sched_stat_runtime
ID: 208
format:
field:unsigned short common_type; offset:0; size:2; signed:0;
field:unsigned char common_flags; offset:2; size:1; signed:0;
field:unsigned char common_preempt_count; offset:3; size:1; signed:0;
field:int common_pid; offset:4; size:4; signed:1;
field:char comm[16]; offset:8; size:16; signed:0;
field:pid_t pid; offset:24; size:4; signed:1;
field:u64 runtime; offset:32; size:8; signed:0;
field:u64 vruntime; offset:40; size:8; signed:0;
print fmt: "comm=%s pid=%d runtime=%Lu [ns] vruntime=%Lu [ns]", REC->comm, REC->pid, (unsigned long long)REC->runtime, (unsigned long long)REC->vruntime
[root@myQEMU sched_stat_runtime]# sched_stat_runtime这个tracepoint有八个域,前4个是通用域,后4个是tracepoint支持域;
cd events/sched/sched_stat_runtime
echo 'comm ~ "sh*"' > filter ///跟踪所有sh开头的进程
130 echo 'pid == 2288' >> filter ///跟踪PID=2288的进程
```
支持类似C语言的表达式对时间进行过滤。
```shell
[root@myQEMU tracing]# cat trace
# tracer: function_graph
#
# CPU DURATION FUNCTION CALLS
# | | | | | | |
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=3255632 [ns] vruntime=110771356247804 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=307728 [ns] vruntime=110771356555532 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=359392 [ns] vruntime=110771356914924 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=635824 [ns] vruntime=110771357550748 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=976800 [ns] vruntime=110771358527548 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=681568 [ns] vruntime=110771359209116 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=896000 [ns] vruntime=110771360105116 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=652272 [ns] vruntime=110771360757388 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=795152 [ns] vruntime=110771361552540 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=739952 [ns] vruntime=110771362292492 [ns] */
0) | /* sched_stat_runtime: comm=sh pid=2288 runtime=812624 [ns] vruntime=110771363105116 [ns] */
0) 添加一个事件
内核各个子系统已经有大量的tracepoint,如果不够,还可以手工添加一个;
在include/trace/events/sched.h添加一个sched_stat_my_runtime的tracepoint
内核提供了宏来方便添加;
DECLARE_EVENT_CLASS(sched_stat_my_runtime,
TP_PROTO(struct task_struct *tsk, u64 vruntime),
TP_ARGS(tsk, vruntime),
TP_STRUCT__entry(
__array( char, comm, TASK_COMM_LEN )
__field( pid_t, pid )
__field( u64, vruntime )
),
TP_fast_assign(
memcpy(__entry->comm, tsk->comm, TASK_COMM_LEN);
__entry->pid = tsk->pid;
__entry->vruntime = vruntime;
),
TP_printk("comm=%s pid=%d minvruntime=%Lu [ns]",
__entry->comm, __entry->pid,
(unsigned long long)__entry->vruntime)
);
DEFINE_EVENT(sched_stat_my_runtime, sched_stat_my_runtime,
TP_PROTO(struct task_struct *tsk, u64 vruntime),
TP_ARGS(tsk, vruntime));
[USER@HOSTNAME tracing]# cat trace
# tracer: nop
#
# entries-in-buffer/entries-written: 239/239 #P:1
#
# _-----=> irqs-off
# / _----=> need-resched
# | / _---=> hardirq/softirq
# || / _--=> preempt-depth
# ||| / delay
# TASK-PID CPU# |||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION
# | | | |||| | |
sh-2287 [000] d... 263.524575: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=sh pid=2287 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
rcu_sched-11 [000] d... 263.526249: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=rcu_sched pid=11 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
rcu_sched-11 [000] d... 263.530214: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=rcu_sched pid=11 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
kworker/0:1-18 [000] d... 263.978131: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=kworker/0:1 pid=18 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
kcompactd0-287 [000] d... 264.010218: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=kcompactd0 pid=287 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
kworker/u2:4-255 [000] d... 264.313158: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=kworker/u2:4 pid=255 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
kworker/u2:4-255 [000] d... 264.313242: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=kworker/u2:4 pid=255 minvruntime=5762812735127 [ns]
sh-2287 [000] d.h. 264.313821: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=sh pid=2287 minvruntime=5762813304551 [ns]
sh-2287 [000] d... 264.314023: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=sh pid=2287 minvruntime=5762813514503 [ns]
kworker/u2:4-255 [000] d... 264.393391: sched_stat_my_runtime: comm=kworker/u2:4 pid=255 minvruntime=5762813514503 [ns]除了DEFINE_EVENT,还可以使用DEFINE_EVENT_CONDITION()定义一个带条件的tracepoint.
如果要定义多个格式相同的tracepoint,可以用DEFINE_EVENT_CLASS()减少代码量;
注:内核提供了一个tracepoint的例子,samples/trace_events/目录中;可以配置CONFIG_samples,CONFIG_SAMPLE_TRACE_EVENTS,编译成模块,加载测试;
案例4:irqs跟踪器
当关闭中断时,CPU不能响应外部事件,如果此时有中断发生,只能在下一次开中断时,才能响应这个外部事件,这段延迟叫“中断延迟”。
ftrace提供irqsoff来跟踪这个延迟;
[root@myQEMU tracing]# echo 0 tracing_on
0 tracing_on
[root@myQEMU tracing]# echo 0 > trace
[root@myQEMU tracing]# echo 0 options/func-trace ///关闭function-trace可以减少一些延迟
0 options/func-trace
[root@myQEMU tracing]# echo irqsoff > current_tracer
[root@myQEMU tracing]# echo 1 > tracing_on
[root@myQEMU tracing]# echo 0 > tracing_on 跟踪结果:
[root@myQEMU tracing]# cat trace
# tracer: irqsoff
#
# irqsoff latency trace v1.1.5 on 5.13.0-rc3+
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
# latency: 2111 us, #158/158, CPU#0 | (M:server VP:0, KP:0, SP:0 HP:0 #P:1)
# -----------------
# | task: sh-2287 (uid:0 nice:0 policy:0 rt_prio:0)
# -----------------
# => started at: n_tty_write
# => ended at: n_tty_write
#
#
# _------=> CPU#
# / _-----=> irqs-off
# | / _----=> need-resched
# || / _---=> hardirq/softirq
# ||| / _--=> preempt-depth
# |||| / delay
# cmd pid ||||| time | caller
# \ / ||||| \ | /
sh-2287 0d... 2us+: uart_write <-n_tty_write
sh-2287 0d... 14us+: start_backtrace <-return_address
sh-2287 0d... 31us+: __uart_start.isra.0 <-uart_write
sh-2287 0d... 45us+: pl011_start_tx <-__uart_start.isra.0
sh-2287 0d... 57us+: pl011_tx_chars <-pl011_start_tx
sh-2287 0d... 70us+: pl011_tx_char <-pl011_tx_chars
sh-2287 0d... 83us+: pl011_read <-pl011_tx_char
...
sh-2287 0d... 1843us+: pl011_read <-pl011_tx_char
sh-2287 0d... 1861us : pl011_tx_char <-pl011_tx_chars
sh-2287 0d... 1869us+: pl011_read <-pl011_tx_char
sh-2287 0d... 1889us : uart_write_wakeup <-pl011_tx_chars
sh-2287 0d... 1899us : tty_port_tty_wakeup <-uart_write_wakeup
sh-2287 0d... 1908us : tty_port_default_wakeup <-tty_port_tty_wakeup
sh-2287 0d... 1918us+: tty_port_tty_get <-tty_port_default_wakeup
sh-2287 0d... 1983us+: tty_wakeup <-tty_port_default_wakeup
sh-2287 0d... 1994us : __wake_up <-tty_wakeup
sh-2287 0d... 2004us : __wake_up_common_lock <-__wake_up
sh-2287 0d... 2014us : __wake_up_common <-__wake_up_common_lock
sh-2287 0d... 2024us : woken_wake_function <-__wake_up_common
sh-2287 0d... 2034us : default_wake_function <-woken_wake_function
sh-2287 0d... 2044us+: try_to_wake_up <-default_wake_function
sh-2287 0d... 2060us+: tty_kref_put <-tty_port_default_wakeup
sh-2287 0d... 2075us+: start_backtrace <-return_address
sh-2287 0d... 2090us+: start_backtrace <-return_address
sh-2287 0d... 2102us+: uart_write <-n_tty_write
sh-2287 0d... 2115us+: tracer_hardirqs_on <-n_tty_write
sh-2287 0d... 2179us : <stack trace>
=> n_tty_write
=> file_tty_write.isra.0
=> redirected_tty_write
=> new_sync_write
=> vfs_write
=> ksys_write
=> __arm64_sys_write
=> invoke_syscall.constprop.0
=> do_el0_svc
=> el0_svc
=> el0_sync_handler
=> el0_sync每个参数的实际意义,参考官网:https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/trace/ftrace.html
案例5:trace marker
trace_marker是一个文件节点,允许用户写入字符串,ftrace会记录写入动作的时间戳;
(1)由于trace_marker是写内存,速度很快,避免串口的长耗时;
(2)可以配合内核的event,跟踪两个trace marker之间,内核的运行状况;
这个可以用来跟踪分析应用程序;
测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/unistd.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <signal.h>
static int mark_fd = 1;
static __thread char buff[BUFSIZ+1];
static void setup_ftrace_marker(void)
{
struct stat st;
char *files[]={
"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_marker",
"/debug/tracing/trace_marker",
"/debugfs/tracing/trace_marker",
};
int ret;
int i=0;
for(i=0; i < (sizeof(files)/sizeof(char*));i++) {
ret = stat(files[i], &st);
if (ret >=0) {
break;
}
}
if (ret >= 0) {
mark_fd = open(files[i], O_WRONLY);
printf("cannot found the sys tracing.\n");
}
return 0;
}
static void ftrace_write(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
int n;
if (mark_fd < 0)
return ;
va_start(ap, fmt);
n = vsnprintf(buff, BUFSIZ, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
write(mark_fd, buff, n);
}
void sig_handler()
{
printf("Oops! will exit...\n");
if (mark_fd >= 0) {
close(mark_fd);
}
_exit(0);
}
int main()
{
printf("hello\n");
int count = 0;
signal(SIGINT,sig_handler);
setup_ftrace_marker();
ftrace_write("start program.\n");
while(1) {
usleep(300*1000);
count++;
ftrace_write("===test count=%d\n",count);
}
return 0;
}执行跟踪:
echo 0 > tracing_on
echo 0 > trace
echo 1 > tracing_on
/mnt/a.out
echo 0 > tracing_on
cat trace查看trace记录
[root@myQEMU tracing]# cat trace
# tracer: nop
#
# entries-in-buffer/entries-written: 33/33 #P:1
#
# _-----=> irqs-off
# / _----=> need-resched
# | / _---=> hardirq/softirq
# || / _--=> preempt-depth
# ||| / delay
# TASK-PID CPU# |||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION
# | | | |||| | |
rb_producer-428 [000] .... 125.274713: ring_buffer_producer_thread: Starting ring buffer hammer
a.out-2291 [000] .... 125.361620: tracing_mark_write: start program.
a.out-2291 [000] .... 125.667714: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=1
a.out-2291 [000] .... 125.970099: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=2
a.out-2291 [000] .... 126.280010: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=3
a.out-2291 [000] .... 126.584222: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=4
a.out-2291 [000] .... 126.886110: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=5
a.out-2291 [000] .... 127.195146: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=6
a.out-2291 [000] .... 127.498109: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=7
a.out-2291 [000] .... 127.802138: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=8
a.out-2291 [000] .... 128.112389: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=9
a.out-2291 [000] .... 128.414082: tracing_mark_write: ===test count=10PS:实际上android的atrace和Trace类,就是基于trace marker实现的;
案例6 wakeup
追踪普通进程从被唤醒到真正得到执行之间的延迟。
echo wakeup > current_tracer
echo 1 > tracing_on
cat trace |head -40案例7 wakeup-rt
跟踪rt进程,从被唤醒到执行的延迟;
echo 0 > tracing_on
echo > trace
echo wakeup_rt > current_tracer
echo 1 > tracing_on
cat trace |head -40当然也可以用脚本来执行这些过程,结果保存到文本:
#!/bin/sh
TRACE_PATH=/sys/kernel/debug/tracing
echo nop > $TRACE_PATH/current_tracer
echo 0 >$TRACE_PATH/tracing_on
echo >$TRACE_PATH/trace
echo 0 > $TRACE_PATH/max_graph_depth
echo $$
#echo $$ > $TRACE_PATH/set_ftrace_pid
echo function_graph > $TRACE_PATH/current_tracer
echo 'blk_update_request' > $TRACE_PATH/set_graph_function
echo 1 > options/func_stack_trace
echo 1 > $TRACE_PATH/tracing_on
exec "$@"3.实用案例:跟踪某个进程的相关函数
实际调试:
如果能把环形队列的数据,写入磁盘,供后续分析,更有现实意义;通过脚本实现?
案例:
跟踪指定进程函数调用
#!/bin/bash
debugfs=/sys/kernel/debug
echo nop > $debugfs/tracing/current_tracer
echo 0 > $debugfs/tracing/tracing_on
echo pidof a.out > $debugfs/tracing/set_ftrace_pid
echo function_graph > $debugfs/tracing/current_tracer
echo vfs_read > $debugfs/tracing/set_graph_function
echo 1 > $debugfs/tracing/tracing_on案例:
当内核log打印输出"min_adj 0"时,保存ftrace信息和kernel log信息到指定目录中:
#!/bin/sh
mkdir -p /data/
echo 8 > /proc/sys/kernel/printk
echo -1000 > /proc/self/oom_score_adj
cd /sys/kernel/debug/tracing
echo 0 > trcing_on
echo 0 > trace
echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/oom/oom_score_adj_update/enable
echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/vmscan/mm_shrink_slab_start/enable
echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/vmscan/mm_shrink_slab_end/enable
#开始采集
echo 1 > tracing_on
TIMES=0
while true
do
dmesg |grep "min_adj 0"
if [ $? -eq 0]
then
cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace > /data/ftrace_.$TIMES
dmesg > /data/kmsg.txt.$TIMES
let TIMES+=1
dmesg -cat
echo > trace
fi
sleep 2
donetrace_cmd和kernelshark
这一组工具,实际上是将上面ftrace的过程,采集记录下来数据,然后图形展示,提供更直观的分析;
trace_cmd,使用遵循reset->record->stop->report模式,简单说用trace_cmd record采集数据,按"ctrl+c"停止采集,在当前目录生成trace.dat文件;用trace-cmd report可以解析trace.dat文件,不过是文字形式的。
下载编译trace-cmd:
git clone https://github.com/rostedt/trace-cmd.git
export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
export ARCH=arm64
makekernelshark,可以将trace.dat文件图形化,方便观察和分析;
实现原理:
Ftrace的设计目标简单,本质上是一种静态代码插装技术,不需要支持某种编程接口让用户自定义 trace 行为。静态代码插装技术更加可靠,不会因为用户的不当使用而导致内核崩溃。 ftrace 代码量很小,稳定可靠。同时Ftrace 有重大的创新:
Ftrace 只需要在函数入口插入一个外部调用:mcount
Ftrace 巧妙的拦截了函数返回的地址,从而可以在运行时先跳到一个事先准备好的统一出口,记录各类信息,然后再返回原来的地址
Ftrace 在链接完成以后,把所有插入点地址都记录到一张表中,然后默认把所有插入点都替换成为空指令(nop),因此默认情况下 Ftrace 的开销几乎是 0
Ftrace 可以在运行时根据需要通过 Sysfs 接口使能和使用,即使在没有第三方工具的情况下也可以方便使用