0.前沿:
1.当前的应用都倾向于内存密集型,物理内存多大都是不够用的,所以必须有页面回收机制;
2.CPU的高速缓存,也是类似页面回收的原理;
1.Linux页面回收的实现原理
当前内核版本5.13,采用的LRU链表算法(不同于经典LRU算法)和第二次机会法;
LRU(Least Recently Used),最少使用算法,根据局部性原理,假定最近使用的页面,会更容易再次用到,最近不使用的页面,将来也不会频繁使用;
1.1LRU链表
Linux为每个内存节点保存一组LRU链表,分别是
enum lru_list {
LRU_INACTIVE_ANON = LRU_BASE,
LRU_ACTIVE_ANON = LRU_BASE + LRU_ACTIVE,
LRU_INACTIVE_FILE = LRU_BASE + LRU_FILE,
LRU_ACTIVE_FILE = LRU_BASE + LRU_FILE + LRU_ACTIVE,
LRU_UNEVICTABLE,
NR_LRU_LISTS
};这样区分的依据是,当内存紧缺时,优先换出文件映射的缓存页面,
因为文件映射只有出现脏页时,才需要回写磁盘;
而匿名页面,必然会回写磁盘。
每个内存节点pglist_data,有一个lruvece成员,指向这些链表;
1.2 lru原理
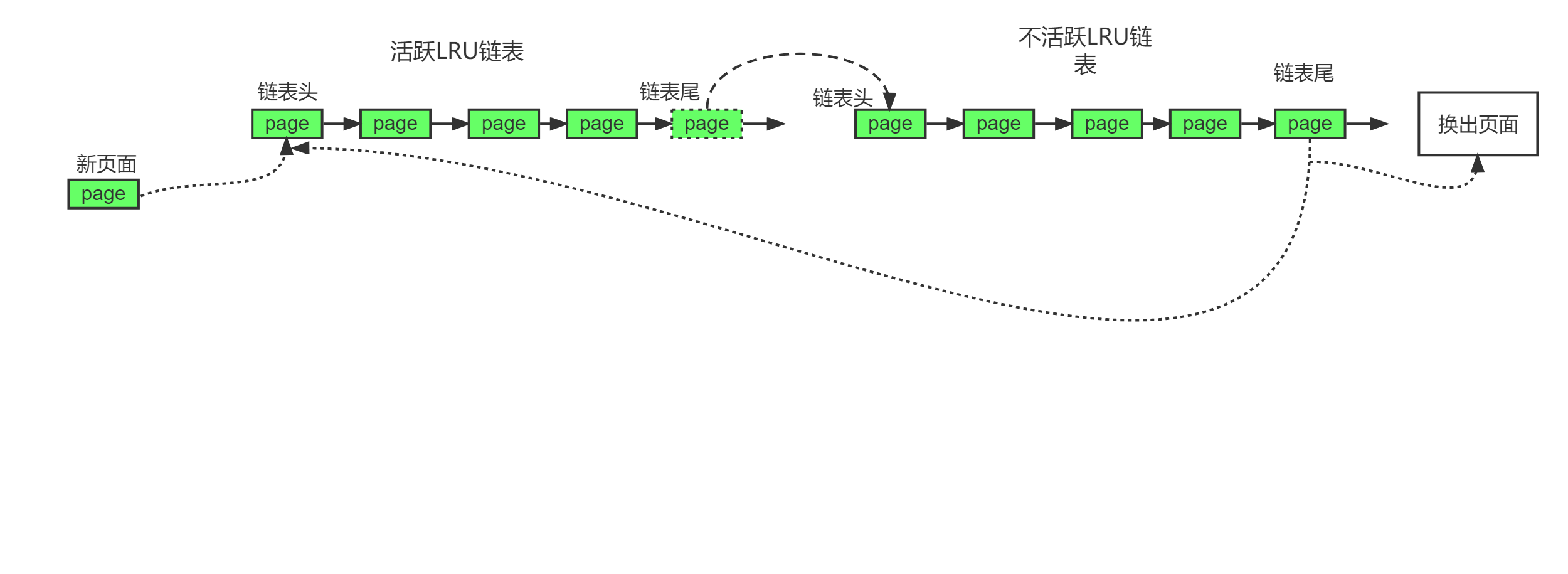
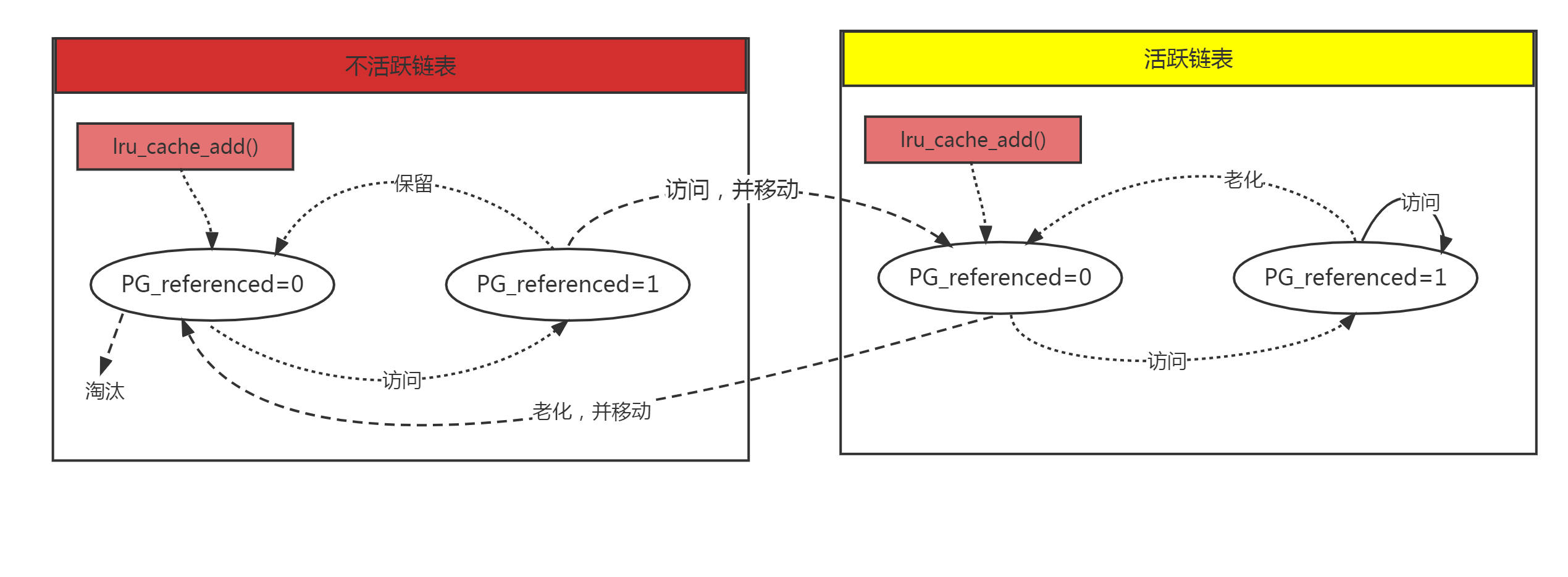
新页面会被添加到活跃链表头,随着老化过程,会被移到不活跃链表头,再移动到链表尾,最后被移除,或者重新添加到活跃Lru链表。
加入LRU函数
void lru_cache_add(struct page *page)
{
struct pagevec *pvec;
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageActive(page) && PageUnevictable(page), page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageLRU(page), page);
get_page(page);
local_lock(&lru_pvecs.lock);
///获取页向量组
pvec = this_cpu_ptr(&lru_pvecs.lru_add);
///将page加入页向量组,并判断是否需要刷新
///这里为提高性能,对page加入lru做了个批处理,一次性加入15个page
if (pagevec_add_and_need_flush(pvec, page))
__pagevec_lru_add(pvec);
local_unlock(&lru_pvecs.lock);
}lru_cache_add->
__pagevec_lru_add->
__pagevec_lru_add_fn->
add_page_to_lru_list(page, lruvec);最总会调用list_add添加到表头
static __always_inline void add_page_to_lru_list(struct page *page,
struct lruvec *lruvec)
{
enum lru_list lru = page_lru(page);
update_lru_size(lruvec, lru, page_zonenum(page), thp_nr_pages(page));
///将page加入到lru链表
list_add(&page->lru, &lruvec->lists[lru]);
}从LRU获取页面接口
///从链表末尾获取页面,LRU实际上实现了FIFO算法
#define lru_to_page(head) (list_entry((head)->prev, struct page, lru)) 可见,LRU链表实际上是实现了FIFO算法,最先进入LRU链表的页面,老化时间最长。
系统运行过程中,页面总是在活跃链表或不活跃链表之间移动的,随着时间推移,不活跃页面会慢慢移动到不活跃链表末尾,这些页面正是页面回收的最合适候选者。
LRU缺陷:
(1)频繁使用的页面,也会被置换出去;
1.3 第二次机会法
第二次机会法,在LRU链表算法基础上,做了一些改进。
核心思想:
在链表尾置换页面时,检查页面的访问位,访问位为0,就淘汰;访问位为1,就给它第二次机会同时将访问位清零;如果该页面被再次访问,访问位会置1,这样被频繁使用的页面,访问位总是1,就不会被淘汰。
linux使用PG_active和PG_referenced两个标志位来实现第二次机会法;
PG_active:表示处于活跃链表;
PG_referenced:软件记录访问标记(实际硬件访问标记从页表的PTE_YOUNG获取)LRU算法图示如下:
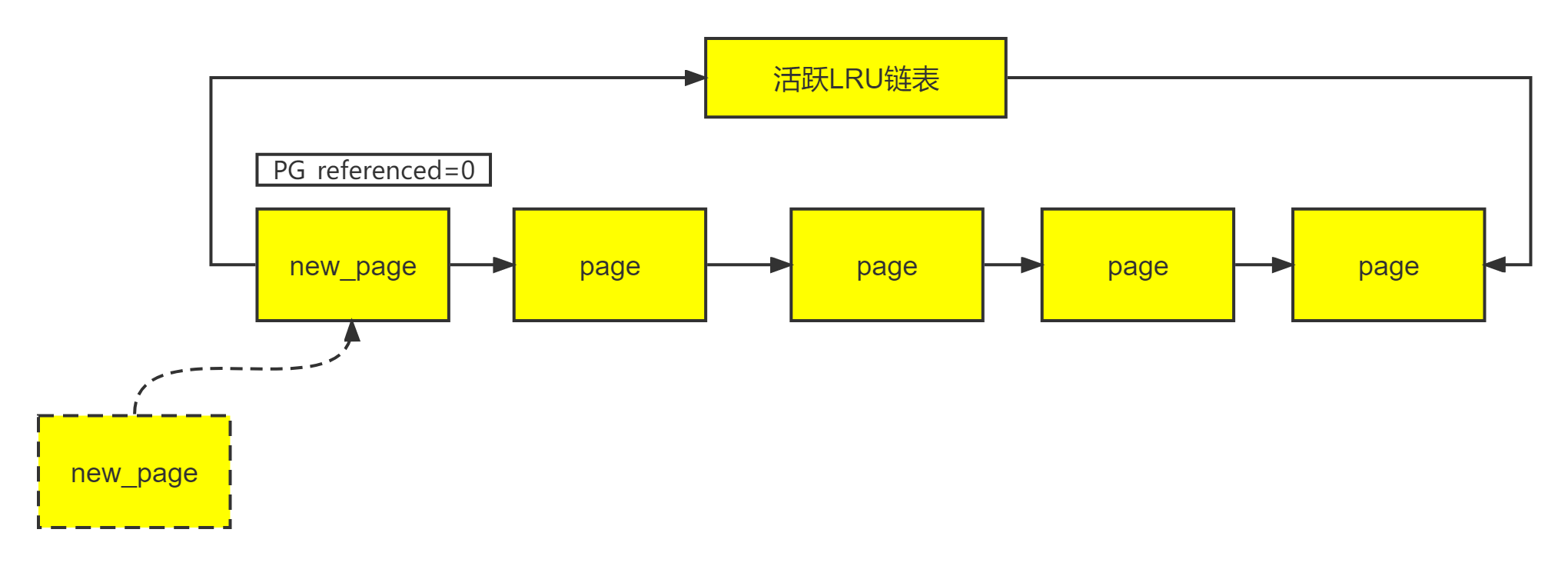
(1)系统中链表原始状态

(2)新分配一个匿名页面:
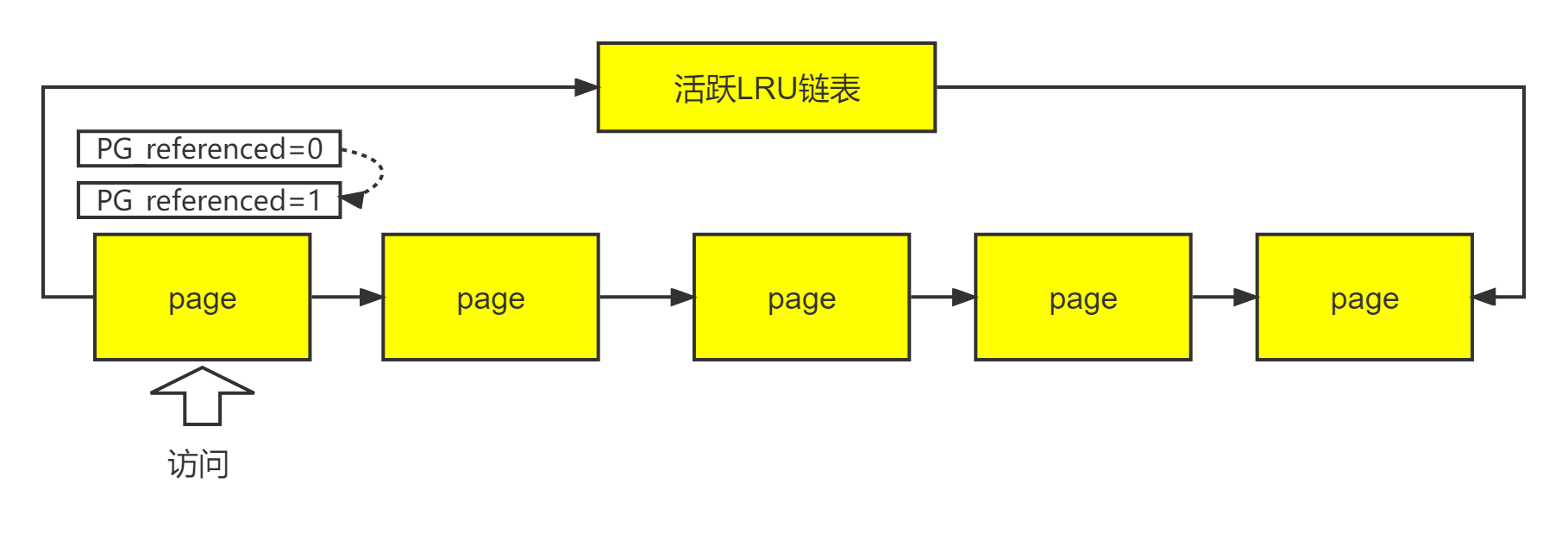
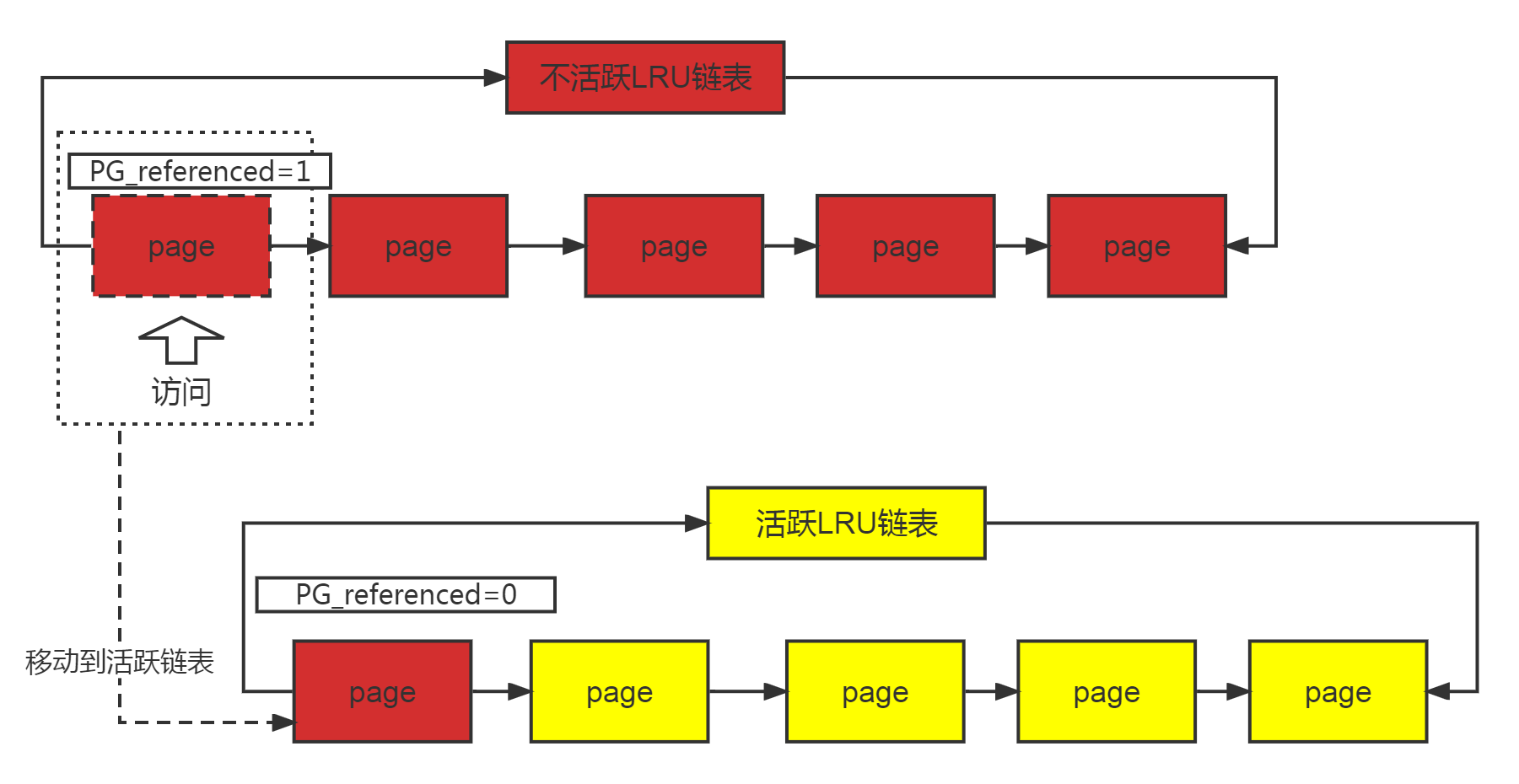
(3)当进程访问一个匿名页面时,根据page所在LRU分别如下操作:
a.访问活跃链表,将PG_referenced置1;
b.访问不活跃链表:
如果PG_referenced为0,将其置1;
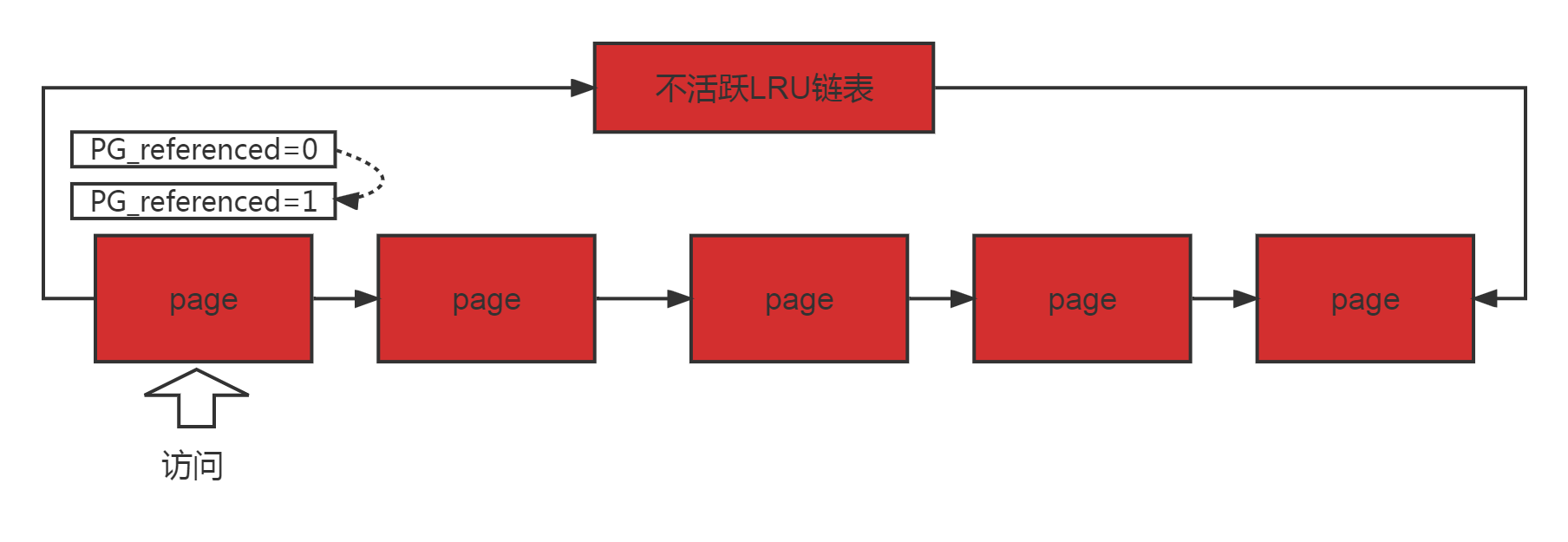
如果PG_referenced为1,将其置0,并且移动到活跃链表;
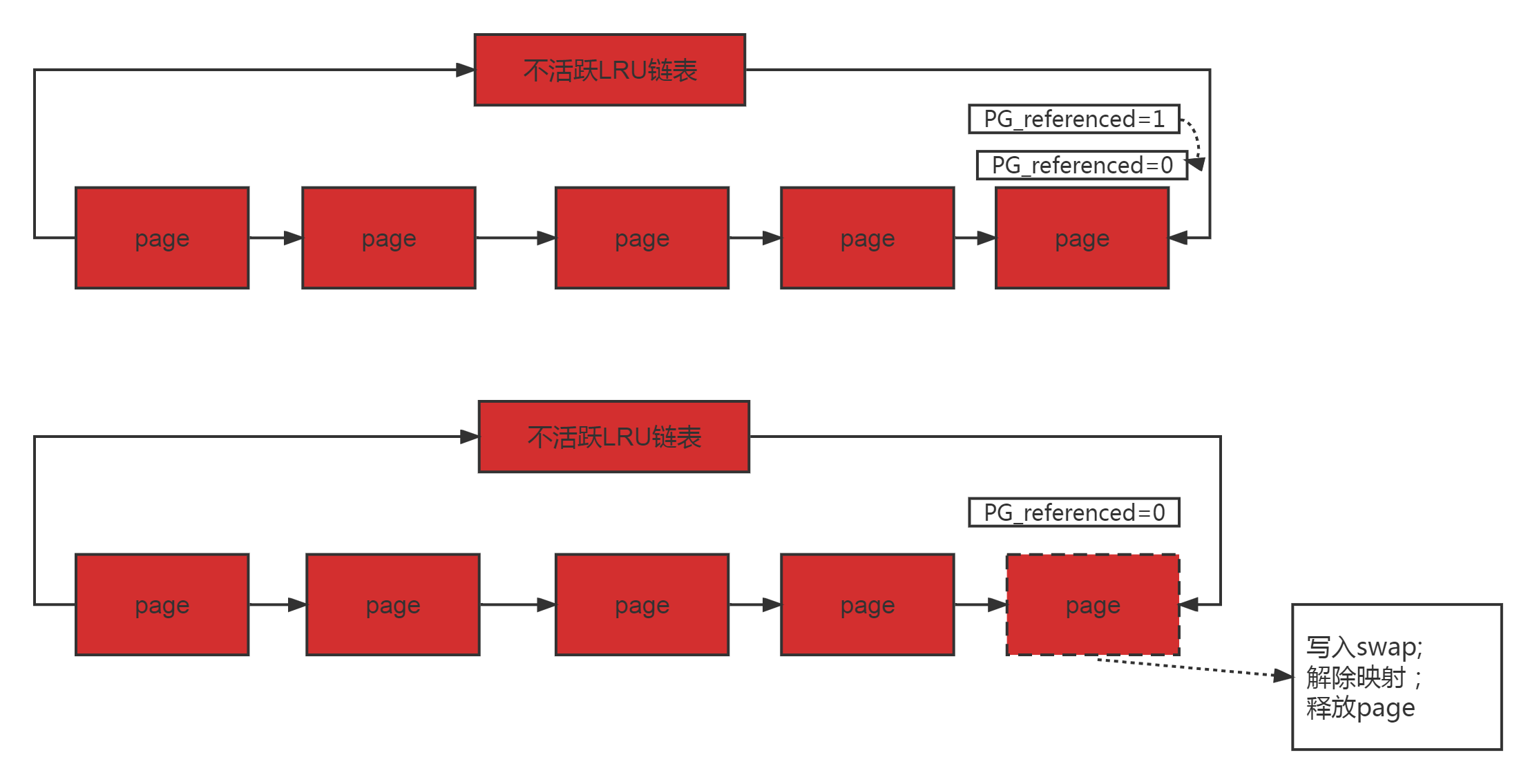
(4)页面淘汰
淘汰页面时,只能从非活跃链表的尾部进行选择;
如果PG_referenced=1,跳过此页,并将PG_referenced清零。
如果PG_referenced=0,将此页写入swap分区,并将所有与此页的映射解除,然后释放。
(5)页面的老化
实现函数:age_active_anon()
活跃链表的页面会有个老化过程,如下
如果页面的 PG_referenced=1,那么把 PG_referenced清零;
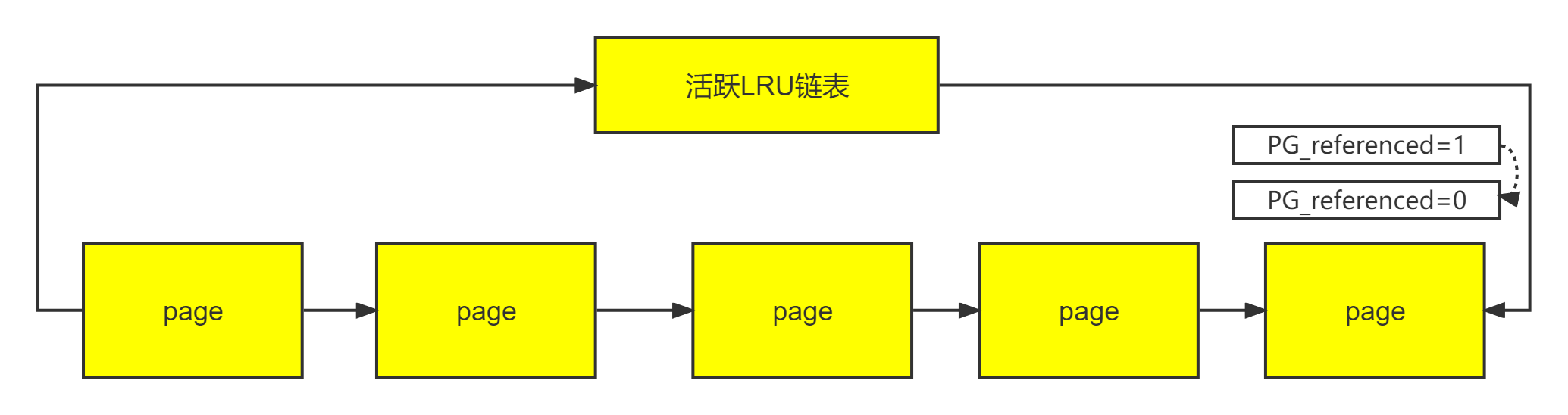
如果页面的 PG_referenced=0,那么把页面移动到不活跃链表;

上述过程流程图:
1.4 对于文件页面的优化
存在这样一个场景,当某个大文件只需要读一次,会造成大量只访问一次的文件缓存页占据在活跃链表中,那在负载较大时,可能导致页面的回收和分配延迟较大;
优化方法:
第一次访问文件时,不调用mark_page_accessed(),访问位PG_referenced=0,放入不活跃链表;
当第一次扫描不活跃LRU链表时,设置访问位PG_referenced=1;
第二次扫描时,发现有访问且PG_referenced=1,则把该页放入活跃链表;
如果没访问,尝试回收;
即用PG_referenced对文件缓存页的访问次数,做一个过滤;
linux2.6.28还做了一个优化,允许一部分活跃页面放在LRU不活跃链表中,扫描不活跃链表时,如果发现匿名页有访问引用PTE,则将该页迁移回活跃链表中;
2.源码解析
Linux实现LRU算法关键函数如下所示:
2.1 mark_page_accessed():
当一个页面被访问时,则调用该函数相应地修改 PG_active 和 PG_referenced。
/*************************************************
* func:标记页面,若页框被访问,被调用
* 有三种情况:
* page在不活跃链表上:
* unreferenced-->inactive,referenced
* referenced -->active,unreferenced
* page在活跃链表上:
* -->active,referenced
*************************************************/
void mark_page_accessed(struct page *page)
{
page = compound_head(page);
///PG_referenced==0,无论活跃或不活跃链表,都置1
if (!PageReferenced(page)) {
SetPageReferenced(page);
} else if (PageUnevictable(page)) {
/*
* Unevictable pages are on the "LRU_UNEVICTABLE" list. But,
* this list is never rotated or maintained, so marking an
* evictable page accessed has no effect.
*/
} else if (!PageActive(page)) {
/*
* If the page is on the LRU, queue it for activation via
* lru_pvecs.activate_page. Otherwise, assume the page is on a
* pagevec, mark it active and it'll be moved to the active
* LRU on the next drain.
*/
///页面被访问,但不是活跃,将访问位清零,加入到活跃链表
///加入到活跃链表:
/// 如果page在当前在lru,先从原来lru删除,再加入也向量组,等待激活;
/// 如果page在页向量组, 激活标志位,将来会加入活跃链表
if (PageLRU(page))
activate_page(page);
else
__lru_cache_activate_page(page);
ClearPageReferenced(page);
workingset_activation(page);
}
if (page_is_idle(page))
clear_page_idle(page);
}__activate_page函数
static void __activate_page(struct page *page, struct lruvec *lruvec)
{
if (!PageActive(page) && !PageUnevictable(page)) {
int nr_pages = thp_nr_pages(page);
del_page_from_lru_list(page, lruvec); ///从不活跃链表删除掉
SetPageActive(page);
add_page_to_lru_list(page, lruvec); ///添加到活跃链表
trace_mm_lru_activate(page);
__count_vm_events(PGACTIVATE, nr_pages);
__count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGACTIVATE,
nr_pages);
}
}2.2page_check_references():
在扫描不活跃LRU链表时会被调用,返回值是一个page_references的枚举类型。
/*******************************************************************************
* func:扫描不活跃链表时,会被调用;返回page_references页面行为类型
* 无页面访问,无映射,回收
* 当页面有访问,引用了PTE时,要放回到活跃LRU链表的情况有:
* (1)页面是匿名页面(PageSwapBacked(page));
* (2)页面位于最近第二次访问的文件缓存,或共享的文件缓存中;
* (3)页面位于可执行文件的缓存中;
*
* 为了解决大量仅使用一次的page cache页面,充斥活跃链表问题,2.6.29开始做了如下优化
* 当第一次读文件时,不调用mark_page_accessed(),
* 即referenced_ptes=1,referenced_page=0
******************************************************************************/
static enum page_references page_check_references(struct page *page,
struct scan_control *sc)
{
int referenced_ptes, referenced_page;
unsigned long vm_flags;
///检查页面,引用了多少个PTE(referenced_ptes)
referenced_ptes = page_referenced(page, 1, sc->target_mem_cgroup,
&vm_flags);
///返回PG_referenced的值,并清除PG_referenced标记
referenced_page = TestClearPageReferenced(page);
/*
* Mlock lost the isolation race with us. Let try_to_unmap()
* move the page to the unevictable list.
*/
///页面被锁,不支持回收
if (vm_flags & VM_LOCKED)
return PAGEREF_RECLAIM;
///referenced_ptes有映射pte
if (referenced_ptes) {
/*
* All mapped pages start out with page table
* references from the instantiating fault, so we need
* to look twice if a mapped file page is used more
* than once.
*
* Mark it and spare it for another trip around the
* inactive list. Another page table reference will
* lead to its activation.
*
* Note: the mark is set for activated pages as well
* so that recently deactivated but used pages are
* quickly recovered.
*/
SetPageReferenced(page);
///referenced_ptes>1, 多个vma映射,放入活跃链表
if (referenced_page || referenced_ptes > 1)
return PAGEREF_ACTIVATE;
/*
* Activate file-backed executable pages after first usage.
*/
///映射可执行文件,放入活跃链表
if ((vm_flags & VM_EXEC) && !PageSwapBacked(page))
return PAGEREF_ACTIVATE;
///referenced_page==0,referenced_ptes==1,继续放在不活跃链表,优化读文件大量一次性page cache占用活跃链表问题
return PAGEREF_KEEP;
}
/* Reclaim if clean, defer dirty pages to writeback */
///没有被访问,也无映射回收页面
if (referenced_page && !PageSwapBacked(page))
return PAGEREF_RECLAIM_CLEAN;
return PAGEREF_RECLAIM;
}2.3page_referenced()
核心思想是利用反响映射系统来统计访问引用pte的用户个数。
///判断页面是否被访问过,并返回引用的PTE个数,即引用这个page的用户进程空间虚拟页面的个数
///就是利用rmap系统来统计引用PTE的个数
int page_referenced(struct page *page,
int is_locked,
struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
unsigned long *vm_flags)
{
int we_locked = 0;
struct page_referenced_arg pra = {
.mapcount = total_mapcount(page),
.memcg = memcg,
};
struct rmap_walk_control rwc = {
.rmap_one = page_referenced_one,
.arg = (void *)&pra,
.anon_lock = page_lock_anon_vma_read,
};
*vm_flags = 0;
if (!pra.mapcount) ///判断_mapcount是否大于等于0
return 0;
if (!page_rmapping(page)) ///判断page->mapping是否有地址空间映射
return 0;
if (!is_locked && (!PageAnon(page) || PageKsm(page))) {
we_locked = trylock_page(page);
if (!we_locked)
return 1;
}
/*
* If we are reclaiming on behalf of a cgroup, skip
* counting on behalf of references from different
* cgroups
*/
if (memcg) {
rwc.invalid_vma = invalid_page_referenced_vma;
}
rmap_walk(page, &rwc); ///遍历映射page的所有VMA,调用rmap_one()函数,判断是否有映射的pte,统计映射pte总数
*vm_flags = pra.vm_flags;
if (we_locked)
unlock_page(page);
return pra.referenced;
}shrink_active_list():
该函数将页面移动到 inactive 链表上去。
3.页面回收的触发
linux触发页面回收有三种情况:
直接回收:alloc_pages()分配物理页,内存紧缺时,会陷入回收机制,同步触发;
周期性回收:当系统内存触发低水位时,唤醒kswapd线程,异步回收内存;
slab收割机制:当内存紧缺时,直接回收,周期性回收,都会调用slab收割机回收,不过这里是内核的内存分配;
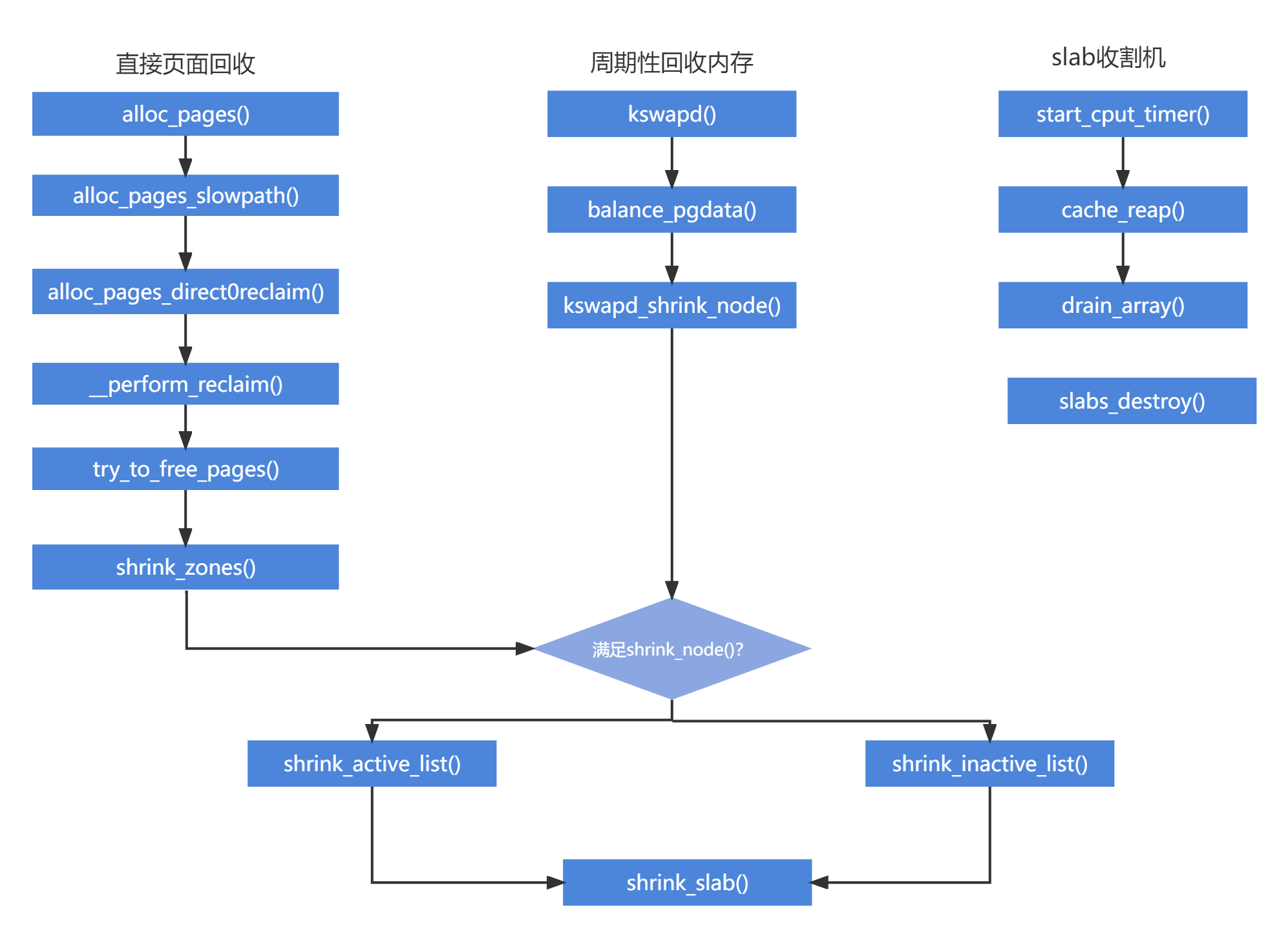
4.kswapd内核线程
4.1 kswapd_wait等待队列
等待队列用于使进程等待某一事件发生,而无需频繁轮询,进程在等待期间睡眠。在某事件发生时,由内核自动唤醒。
setup_arch()-->
paging_init()-->
bootmem_init()->
zone_sizes_init()-->
free_area_init_node()-->
free_area_init_core()kswapd_wait等待队列在free_area_init_core中进行初始化,每个内存节点一个。
kswapd内核线程在kswapd_wait等待队列上等待TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE事件发生。
static void __paginginit free_area_init_core(struct pglist_data *pgdat,
unsigned long node_start_pfn, unsigned long node_end_pfn,
unsigned long *zones_size, unsigned long *zholes_size)
{
...
init_waitqueue_head(&pgdat->kswapd_wait);
init_waitqueue_head(&pgdat->pfmemalloc_wait);
pgdat_page_ext_init(pgdat);
...
}4.2kswapd内核线程
kswapd内核线程负责在内存不足的情况下进行页面回收,为每NUMA内存节点创建一个"kswap%d"的内核线程。
其中kswapd函数是内核线程kswapd的入口。
/*
* 一个pglist_data,对应一个内存节点,是最顶层的内存管理数据结构
* 主要包括三部分:
* 1.描述zone
* 2.描述内存节点的信息;
* 3.和页面回收相关;
*/
typedef struct pglist_data {
int node_id;
wait_queue_head_t kswapd_wait;
struct task_struct *kswapd; /* Protected by
mem_hotplug_begin/end() */
int kswapd_order;
enum zone_type kswapd_highest_zoneidx;
struct lruvec __lruvec; ///lru链表向量(包括所有,5种lru链表)
} pg_data_t;wakeup_kswapd唤醒kswaped内核线程
分配内存路径上的唤醒函数wakeup_kswapd把kswapd_order和kswapd_highest_zoneidx作为参数传递给kswaped内核线程;
alloc_page()->
__alloc_pages_nodemask()->
__alloc_pages_slowpth()->
wake_all_kswapds()->
wakeup_kswapd()void wakeup_kswapd(struct zone *zone, gfp_t gfp_flags, int order,
enum zone_type highest_zoneidx)
{
pg_data_t *pgdat;
enum zone_type curr_idx;
if (!managed_zone(zone))
return;
if (!cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_flags))
return;
pgdat = zone->zone_pgdat;
///准备本内存节点的kswapd_order和kswapd_highest_zoneidx
curr_idx = READ_ONCE(pgdat->kswapd_highest_zoneidx);
if (curr_idx == MAX_NR_ZONES || curr_idx < highest_zoneidx)
WRITE_ONCE(pgdat->kswapd_highest_zoneidx, highest_zoneidx);
if (READ_ONCE(pgdat->kswapd_order) < order)
WRITE_ONCE(pgdat->kswapd_order, order);
if (!waitqueue_active(&pgdat->kswapd_wait))
return;
/* Hopeless node, leave it to direct reclaim if possible */
if (pgdat->kswapd_failures >= MAX_RECLAIM_RETRIES ||
(pgdat_balanced(pgdat, order, highest_zoneidx) &&
!pgdat_watermark_boosted(pgdat, highest_zoneidx))) {
/*
* There may be plenty of free memory available, but it's too
* fragmented for high-order allocations. Wake up kcompactd
* and rely on compaction_suitable() to determine if it's
* needed. If it fails, it will defer subsequent attempts to
* ratelimit its work.
*/
if (!(gfp_flags & __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM))
wakeup_kcompactd(pgdat, order, highest_zoneidx);
return;
}
trace_mm_vmscan_wakeup_kswapd(pgdat->node_id, highest_zoneidx, order,
gfp_flags);
///唤醒kswapd_wait队列
wake_up_interruptible(&pgdat->kswapd_wait);
}回收函数kswapd
static int kswapd(void *p)
{
...
///PF_MEMALLOC允许使用系统预留内存,即不考虑水位
tsk->flags |= PF_MEMALLOC | PF_SWAPWRITE | PF_KSWAPD;
for ( ; ; ) {
bool ret;
///回收页面数量,2的order次幂
alloc_order = reclaim_order = READ_ONCE(pgdat->kswapd_order);
///classzone_idx内核线程扫描和回收的最高zone
highest_zoneidx = kswapd_highest_zoneidx(pgdat,
highest_zoneidx);
kswapd_try_sleep:
///睡眠,等待wakeup_kswapd唤醒
kswapd_try_to_sleep(pgdat, alloc_order, reclaim_order,
highest_zoneidx);
...
reclaim_order = balance_pgdat(pgdat, alloc_order,
highest_zoneidx);
if (reclaim_order < alloc_order)
goto kswapd_try_sleep;
}
tsk->flags &= ~(PF_MEMALLOC | PF_SWAPWRITE | PF_KSWAPD);
return 0;
}4.3 kswapd内核线程扫描过程
kswapd扫描
kswapd()->balance_pgdat()
/*****************************************************************************
* 回收页面的主函数:
*
* highmem->normal->dma, 从高端往低端方向,查找处于不平衡状态,
* 即free_pages <= high_wmark_pagesend_zone的zone
*
*
****************************************************************************/
static int balance_pgdat(pg_data_t *pgdat, int order, int highest_zoneidx)
{
///用于内存碎片化
unsigned long nr_boost_reclaim;
...
nr_boost_reclaim = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= highest_zoneidx; i++) {
zone = pgdat->node_zones + i;
if (!managed_zone(zone))
continue;
nr_boost_reclaim += zone->watermark_boost;
zone_boosts[i] = zone->watermark_boost;
}
boosted = nr_boost_reclaim;
restart:
sc.priority = DEF_PRIORITY;
do {
...
///检查这个节点中是否有合格的zone,其水位高于高水位且能分配2的sc.order次幂个连续的物理页面
balanced = pgdat_balanced(pgdat, sc.order, highest_zoneidx);
///若所有zone都不合格,关闭nr_boost_reclaim,重新检查一次
if (!balanced && nr_boost_reclaim) {
nr_boost_reclaim = 0;
goto restart;
}
//若符合条件,不需要回收,直接跳出
if (!nr_boost_reclaim && balanced)
goto out;
...
///老化匿名页面的活跃链表
age_active_anon(pgdat, &sc);
...
///真正扫描和页回收函数,扫描的参数和结果存放在struct scan_control中,
///返回true表明回收了所需要的页面,不需要再提高扫描优先级
if (kswapd_shrink_node(pgdat, &sc))
raise_priority = false;
...
///加大扫描粒度
if (raise_priority || !nr_reclaimed)
sc.priority--;
} while (sc.priority >= 1);
...
out:
/* If reclaim was boosted, account for the reclaim done in this pass */
///若设置了nr_boost_reclaim,唤醒kcompacted线程
if (boosted) {
...
wakeup_kcompactd(pgdat, pageblock_order, highest_zoneidx);
}
...
return sc.order;
}对活跃链表中页面的老化
kswapd()->balance_pgdat()->age_active_anon()
///老化匿名页面的活跃链表
static void age_active_anon(struct pglist_data *pgdat,
struct scan_control *sc)
{
struct mem_cgroup *memcg;
struct lruvec *lruvec;
if (!total_swap_pages)
return;
lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(NULL, pgdat);
if (!inactive_is_low(lruvec, LRU_INACTIVE_ANON))
return;
memcg = mem_cgroup_iter(NULL, NULL, NULL);
do {
lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(memcg, pgdat);
shrink_active_list(SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX, lruvec,
sc, LRU_ACTIVE_ANON);
memcg = mem_cgroup_iter(NULL, memcg, NULL);
} while (memcg);
}执行回收
kswapd()->balance_pgdat()->kswapd_shrink_node()->shrink_node()->shrink_node_memcgs()
static void shrink_node_memcgs(pg_data_t *pgdat, struct scan_control *sc)
{
struct mem_cgroup *target_memcg = sc->target_mem_cgroup;
struct mem_cgroup *memcg;
memcg = mem_cgroup_iter(target_memcg, NULL, NULL);
do {
///获取LRU链表的集合
struct lruvec *lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(memcg, pgdat);
unsigned long reclaimed;
unsigned long scanned;
/*
* This loop can become CPU-bound when target memcgs
* aren't eligible for reclaim - either because they
* don't have any reclaimable pages, or because their
* memory is explicitly protected. Avoid soft lockups.
*/
cond_resched();
mem_cgroup_calculate_protection(target_memcg, memcg);
if (mem_cgroup_below_min(memcg)) {
/*
* Hard protection.
* If there is no reclaimable memory, OOM.
*/
continue;
} else if (mem_cgroup_below_low(memcg)) {
/*
* Soft protection.
* Respect the protection only as long as
* there is an unprotected supply
* of reclaimable memory from other cgroups.
*/
if (!sc->memcg_low_reclaim) {
sc->memcg_low_skipped = 1;
continue;
}
memcg_memory_event(memcg, MEMCG_LOW);
}
reclaimed = sc->nr_reclaimed;
scanned = sc->nr_scanned;
///扫描回收lru链表
shrink_lruvec(lruvec, sc);
///扫描回收slab链表
shrink_slab(sc->gfp_mask, pgdat->node_id, memcg,
sc->priority);
/* Record the group's reclaim efficiency */
vmpressure(sc->gfp_mask, memcg, false,
sc->nr_scanned - scanned,
sc->nr_reclaimed - reclaimed);
} while ((memcg = mem_cgroup_iter(target_memcg, memcg, NULL)));
}回收函数shrink_lruvec()
static void shrink_lruvec(struct lruvec *lruvec, struct scan_control *sc)
{
unsigned long nr[NR_LRU_LISTS];
unsigned long targets[NR_LRU_LISTS];
unsigned long nr_to_scan;
enum lru_list lru;
unsigned long nr_reclaimed = 0;
unsigned long nr_to_reclaim = sc->nr_to_reclaim;
struct blk_plug plug;
bool scan_adjusted;
///计算每个链表应该扫描的页面数量,结果放在nr[]
get_scan_count(lruvec, sc, nr);
///全局回收,优化当内存紧缺时,触发直接回收
scan_adjusted = (!cgroup_reclaim(sc) && !current_is_kswapd() &&
sc->priority == DEF_PRIORITY);
///遍历所有链表,回收页面
///主要处理不活跃匿名页面,活跃文件映射页面和不活跃文件映射页面
while (nr[LRU_INACTIVE_ANON] || nr[LRU_ACTIVE_FILE] ||
nr[LRU_INACTIVE_FILE]) {
unsigned long nr_anon, nr_file, percentage;
unsigned long nr_scanned;
for_each_evictable_lru(lru) {
if (nr[lru]) {
nr_to_scan = min(nr[lru], SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX);
nr[lru] -= nr_to_scan;
//扫描链表,回收页面,返回成功回收的页面数量
nr_reclaimed += shrink_list(lru, nr_to_scan,
lruvec, sc);
}
}
cond_resched();
///没完成回收任务,或设置了scan_adjusted,继续进行页面扫描
if (nr_reclaimed < nr_to_reclaim || scan_adjusted)
continue;
...
scan_adjusted = true;
}
blk_finish_plug(&plug);
sc->nr_reclaimed += nr_reclaimed;
///老化活跃链表
///如果不活跃链表页面数量太少,从活跃链表迁移一部分页面到不活跃链表
if (total_swap_pages && inactive_is_low(lruvec, LRU_INACTIVE_ANON))
shrink_active_list(SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX, lruvec,
sc, LRU_ACTIVE_ANON);
}shrink_lruvec()->shrink_list()
static unsigned long shrink_list(enum lru_list lru, unsigned long nr_to_scan,
struct lruvec *lruvec, struct scan_control *sc)
{
if (is_active_lru(lru)) {
///扫描活跃的文件映射链表
if (sc->may_deactivate & (1 << is_file_lru(lru)))
shrink_active_list(nr_to_scan, lruvec, sc, lru);
else
sc->skipped_deactivate = 1;
return 0;
}
///扫描不活跃链表
return shrink_inactive_list(nr_to_scan, lruvec, sc, lru);
}扫描活跃链表函数shrink_active_list()实现:
/*************************************************************************************
* func:扫描活跃链表,包括匿名页或文件映射页面,
* 把最近没访问的页面,从活跃链表尾部移到不活跃链表头部
* nr_to_scan: 待扫描页面的数量
* lruvec:LRU链表集合
* sc:页面扫描控制参数
* lru: 待扫描的LRU链表类型
*************************************************************************************/
static void shrink_active_list(unsigned long nr_to_scan,
struct lruvec *lruvec,
struct scan_control *sc,
enum lru_list lru)
{
unsigned long nr_taken;
unsigned long nr_scanned;
unsigned long vm_flags;
///定义三个临时链表
LIST_HEAD(l_hold); /* The pages which were snipped off */
LIST_HEAD(l_active);
LIST_HEAD(l_inactive);
struct page *page;
unsigned nr_deactivate, nr_activate;
unsigned nr_rotated = 0;
///判断是否为文件映射链表
int file = is_file_lru(lru);
///获取内存节点
struct pglist_data *pgdat = lruvec_pgdat(lruvec);
lru_add_drain();
spin_lock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
///将页面批量迁移到临时链表l_hold中
nr_taken = isolate_lru_pages(nr_to_scan, lruvec, &l_hold,
&nr_scanned, sc, lru);
///增加内存节点NR_ISOLATED_ANON计数
__mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + file, nr_taken);
if (!cgroup_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(PGREFILL, nr_scanned);
__count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGREFILL, nr_scanned);
spin_unlock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
///扫描临时链表l_hold,有些页面放到不活跃链表,有些会放回到活跃链表
while (!list_empty(&l_hold)) {
cond_resched();
page = lru_to_page(&l_hold);
list_del(&page->lru);
///如果不能回收,放入不能回收链表
if (unlikely(!page_evictable(page))) {
putback_lru_page(page);
continue;
}
if (unlikely(buffer_heads_over_limit)) {
if (page_has_private(page) && trylock_page(page)) {
if (page_has_private(page))
try_to_release_page(page, 0);
unlock_page(page);
}
}
///page_referenced()返回该页面最近访问,应用pte个数,若返回0,表示最近没访问
if (page_referenced(page, 0, sc->target_mem_cgroup,
&vm_flags)) {
/*
* Identify referenced, file-backed active pages and
* give them one more trip around the active list. So
* that executable code get better chances to stay in
* memory under moderate memory pressure. Anon pages
* are not likely to be evicted by use-once streaming
* IO, plus JVM can create lots of anon VM_EXEC pages,
* so we ignore them here.
*/
if ((vm_flags & VM_EXEC) && page_is_file_lru(page)) {
nr_rotated += thp_nr_pages(page);
///放回活跃链表
list_add(&page->lru, &l_active);
continue;
}
}
ClearPageActive(page); /* we are de-activating */
SetPageWorkingset(page);
///加入不活跃链表
list_add(&page->lru, &l_inactive);
}
/*
* Move pages back to the lru list.
*/
spin_lock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
///将l_active,l_inactive分别加入到相应的链表
nr_activate = move_pages_to_lru(lruvec, &l_active);
nr_deactivate = move_pages_to_lru(lruvec, &l_inactive);
/* Keep all free pages in l_active list */
list_splice(&l_inactive, &l_active);
__count_vm_events(PGDEACTIVATE, nr_deactivate);
__count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGDEACTIVATE, nr_deactivate);
__mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + file, -nr_taken);
spin_unlock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
mem_cgroup_uncharge_list(&l_active);
free_unref_page_list(&l_active);
trace_mm_vmscan_lru_shrink_active(pgdat->node_id, nr_taken, nr_activate,
nr_deactivate, nr_rotated, sc->priority, file);
}扫描不活跃链表shrink_inactive_list()实现:
///扫描不活跃LRU链表,尝试回收页面,返回已经回收的页面数量
static noinline_for_stack unsigned long
shrink_inactive_list(unsigned long nr_to_scan, struct lruvec *lruvec,
struct scan_control *sc, enum lru_list lru)
{
LIST_HEAD(page_list);
unsigned long nr_scanned;
unsigned int nr_reclaimed = 0;
unsigned long nr_taken;
struct reclaim_stat stat;
bool file = is_file_lru(lru);
enum vm_event_item item;
struct pglist_data *pgdat = lruvec_pgdat(lruvec);
bool stalled = false;
while (unlikely(too_many_isolated(pgdat, file, sc))) {
if (stalled)
return 0;
/* wait a bit for the reclaimer. */
///太多进程在直接回收页面,睡眠,避免内存抖动
msleep(100);
stalled = true;
/* We are about to die and free our memory. Return now. */
if (fatal_signal_pending(current))
return SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX;
}
lru_add_drain();
spin_lock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
///分离页面到临时页表
nr_taken = isolate_lru_pages(nr_to_scan, lruvec, &page_list,
&nr_scanned, sc, lru);
///增加内存节点NR_ISOLATED_ANON计数
__mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + file, nr_taken);
item = current_is_kswapd() ? PGSCAN_KSWAPD : PGSCAN_DIRECT;
if (!cgroup_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(item, nr_scanned);
__count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), item, nr_scanned);
__count_vm_events(PGSCAN_ANON + file, nr_scanned);
spin_unlock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
if (nr_taken == 0)
return 0;
///执行回收页面,返回nr_reclaimed个
nr_reclaimed = shrink_page_list(&page_list, pgdat, sc, &stat, false);
spin_lock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
///page_list链表剩余页面迁回不活跃链表
move_pages_to_lru(lruvec, &page_list);
///减少NR_ISOLATED_ANON计数
__mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + file, -nr_taken);
item = current_is_kswapd() ? PGSTEAL_KSWAPD : PGSTEAL_DIRECT;
if (!cgroup_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(item, nr_reclaimed);
__count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), item, nr_reclaimed);
__count_vm_events(PGSTEAL_ANON + file, nr_reclaimed);
spin_unlock_irq(&lruvec->lru_lock);
lru_note_cost(lruvec, file, stat.nr_pageout);
mem_cgroup_uncharge_list(&page_list);
free_unref_page_list(&page_list);
/*
* If dirty pages are scanned that are not queued for IO, it
* implies that flushers are not doing their job. This can
* happen when memory pressure pushes dirty pages to the end of
* the LRU before the dirty limits are breached and the dirty
* data has expired. It can also happen when the proportion of
* dirty pages grows not through writes but through memory
* pressure reclaiming all the clean cache. And in some cases,
* the flushers simply cannot keep up with the allocation
* rate. Nudge the flusher threads in case they are asleep.
*/
if (stat.nr_unqueued_dirty == nr_taken)
wakeup_flusher_threads(WB_REASON_VMSCAN);
sc->nr.dirty += stat.nr_dirty;
sc->nr.congested += stat.nr_congested;
sc->nr.unqueued_dirty += stat.nr_unqueued_dirty;
sc->nr.writeback += stat.nr_writeback;
sc->nr.immediate += stat.nr_immediate;
sc->nr.taken += nr_taken;
if (file)
sc->nr.file_taken += nr_taken;
trace_mm_vmscan_lru_shrink_inactive(pgdat->node_id,
nr_scanned, nr_reclaimed, &stat, sc->priority, file);
return nr_reclaimed;
}4.4 LRU页面跟踪
操作lru链表是一个并发过程,在维护链表时,如何避免页面被其他进程释放?
通过page->_refcount计数,来维护page的并发问题;