Keras图片增强
CNN中图片具有平移不变形,旋转不变形,如下图,而在实际应用中训练数据常常不足, 或不均衡, 因此我们可以通过增强数据,扩展训练集。
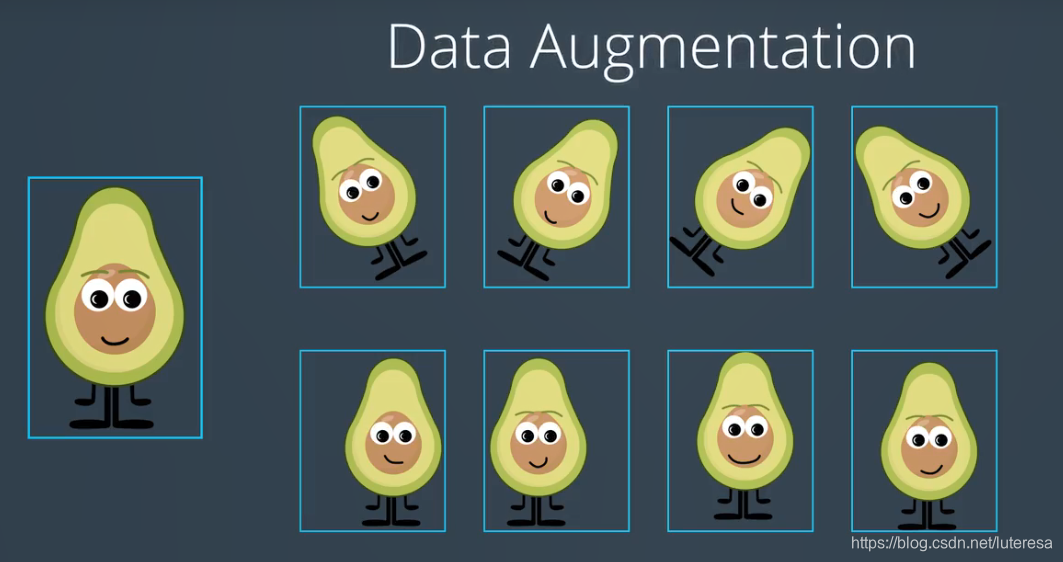
我们可以对现有的数据,进行平移、翻转、旋转、缩放、亮度增强等操作,以生成新的图片来参与训练或测试。
这种操作可以将图片数量提升数倍,由此大大降低了过拟合的可能,因为模型训练了更多的图片,有更好的泛化。
实际上经验,图像增强中使用旋转、翻转,效果不错;
https://keras.io/preprocessing/image/
https://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/preprocessing/image/
https://machinelearningmastery.com/image-augmentation-deep-learning-keras/
https://blog.keras.io/building-powerful-image-classification-models-using-very-little-data.html
Keras中数据增强的类:ImageDataGenerator
keras.preprocessing.image.ImageDataGenerator(featurewise_center=False,
samplewise_center=False,
featurewise_std_normalization=False,
samplewise_std_normalization=False,
zca_whitening=False,
zca_epsilon=1e-6,
rotation_range=0.,
width_shift_range=0.,
height_shift_range=0.,
shear_range=0.,
zoom_range=0.,
channel_shift_range=0.,
fill_mode='nearest',
cval=0.,
horizontal_flip=False,
vertical_flip=False,
rescale=None,
preprocessing_function=None,
data_format=K.image_data_format())参数
featurewise_center:布尔值,使输入数据集去中心化(均值为0), 按feature执行
samplewise_center:布尔值,使输入数据的每个样本均值为0
featurewise_std_normalization:布尔值,将输入除以数据集的标准差以完成标准化, 按feature执行
samplewise_std_normalization:布尔值,将输入的每个样本除以其自身的标准差
zca_whitening:布尔值,对输入数据施加ZCA白化
zca_epsilon: ZCA使用的eposilon,默认1e-6
rotation_range:整数,数据提升时图片随机转动的角度
width_shift_range:浮点数,图片宽度的某个比例,数据提升时图片水平偏移的幅度
height_shift_range:浮点数,图片高度的某个比例,数据提升时图片竖直偏移的幅度
shear_range:浮点数,剪切强度(逆时针方向的剪切变换角度)
zoom_range:浮点数或形如[lower,upper]的列表,随机缩放的幅度,若为浮点数,则相当于[lower,upper] = [1 - zoom_range, 1+zoom_range]
channel_shift_range:浮点数,随机通道偏移的幅度
fill_mode:;‘constant’,‘nearest’,‘reflect’或‘wrap’之一,当进行变换时超出边界的点将根据本参数给定的方法进行处理
cval:浮点数或整数,当fill_mode=constant时,指定要向超出边界的点填充的值
horizontal_flip:布尔值,进行随机水平翻转
vertical_flip:布尔值,进行随机竖直翻转
rescale: 重放缩因子,默认为None. 如果为None或0则不进行放缩,否则会将该数值乘到数据上(在应用其他变换之前)
preprocessing_function: 将被应用于每个输入的函数。该函数将在图片缩放和数据提升之后运行。该函数接受一个参数,为一张图片(秩为3的numpy array),并且输出一个具有相同shape的numpy array
data_format:字符串,“channel_first”或“channel_last”之一,代表图像的通道维的位置。该参数是Keras 1.x中的image_dim_ordering,“channel_last”对应原本的“tf”,“channel_first”对应原本的“th”。以128x128的RGB图像为例,“channel_first”应将数据组织为(3,128,128),而“channel_last”应将数据组织为(128,128,3)。该参数的默认值是~/.keras/keras.json中设置的值,若从未设置过,则为“channel_last”
方法
fit(x, augment=False, rounds=1):计算依赖于数据的变换所需要的统计信息(均值方差等),只有使用featurewise_center,featurewise_std_normalization或zca_whitening时需要此函数。
X:numpy array,样本数据,秩应为4.在黑白图像的情况下channel轴的值为1,在彩色图像情况下值为3
augment:布尔值,确定是否使用随即提升过的数据
round:若设augment=True,确定要在数据上进行多少轮数据提升,默认值为1
seed: 整数,随机数种子
flow(self, X, y, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, seed=None, save_to_dir=None, save_prefix='', save_format='png'):接收numpy数组和标签为参数,生成经过数据提升或标准化后的batch数据,并在一个无限循环中不断的返回batch数据
x:样本数据,秩应为4.在黑白图像的情况下channel轴的值为1,在彩色图像情况下值为3
y:标签
batch_size:整数,默认32
shuffle:布尔值,是否随机打乱数据,默认为True
save_to_dir:None或字符串,该参数能让你将提升后的图片保存起来,用以可视化
save_prefix:字符串,保存提升后图片时使用的前缀, 仅当设置了save_to_dir时生效
save_format:"png"或"jpeg"之一,指定保存图片的数据格式,默认"jpeg"
yields:形如(x,y)的tuple,x是代表图像数据的numpy数组.y是代表标签的numpy数组.该迭代器无限循环.
seed: 整数,随机数种子
flow_from_directory(directory): 以文件夹路径为参数,生成经过数据提升/归一化后的数据,在一个无限循环中无限产生batch数据
directory: 目标文件夹路径,对于每一个类,该文件夹都要包含一个子文件夹.子文件夹中任何JPG、PNG、BNP、PPM的图片都会被生成器使用.详情请查看此脚本
target_size: 整数tuple,默认为(256, 256). 图像将被resize成该尺寸
color_mode: 颜色模式,为"grayscale","rgb"之一,默认为"rgb".代表这些图片是否会被转换为单通道或三通道的图片.
classes: 可选参数,为子文件夹的列表,如['dogs','cats']默认为None. 若未提供,则该类别列表将从directory下的子文件夹名称/结构自动推断。每一个子文件夹都会被认为是一个新的类。(类别的顺序将按照字母表顺序映射到标签值)。通过属性class_indices可获得文件夹名与类的序号的对应字典。
class_mode: "categorical", "binary", "sparse"或None之一. 默认为"categorical. 该参数决定了返回的标签数组的形式, "categorical"会返回2D的one-hot编码标签,"binary"返回1D的二值标签."sparse"返回1D的整数标签,如果为None则不返回任何标签, 生成器将仅仅生成batch数据, 这种情况在使用
model.predict_generator()和model.evaluate_generator()等函数时会用到.
batch_size: batch数据的大小,默认32
shuffle: 是否打乱数据,默认为True
seed: 可选参数,打乱数据和进行变换时的随机数种子
save_to_dir: None或字符串,该参数能让你将提升后的图片保存起来,用以可视化
save_prefix:字符串,保存提升后图片时使用的前缀, 仅当设置了save_to_dir时生效
save_format:"png"或"jpeg"之一,指定保存图片的数据格式,默认"jpeg"
flollow_links: 是否访问子文件夹中的软链接
1.ImageDataGenerator数据增强方法
from numpy import expand_dims
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from matplotlib import pyplot
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from keras.preprocessing import image
import keras as K# load the image
img = image.load_img('bird.jpg')
print(img)
# convert to numpy array
data = image.img_to_array(img)
print(data.shape)
pyplot.imshow(img)
(399, 640, 3)

# expand dimension to one sample
samples = expand_dims(data, 0)
print(samples.shape)(1, 399, 640, 3)1.1 随机平移
移动范围可以用像素点,也可以用0~1浮点数,表示移动比例
# create image data augmentation generator
#datagen = ImageDataGenerator(width_shift_range=[-200,200])
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(width_shift_range=0.5,height_shift_range=0.5)
# prepare iterator
it = datagen.flow(samples, batch_size=1)
# generate samples and plot
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# generate batch of images
batch = it.next()
# convert to unsigned integers for viewing
image = batch[0].astype('uint8')
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(image)
# show the figure
pyplot.show()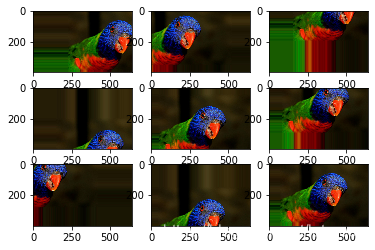
1.2 水平或垂直翻转
# create image data augmentation generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(horizontal_flip=True,vertical_flip=True)
# prepare iterator
it = datagen.flow(samples, batch_size=1)
# generate samples and plot
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# generate batch of images
batch = it.next()
# convert to unsigned integers for viewing
image = batch[0].astype('uint8')
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(image)
# show the figure
pyplot.show()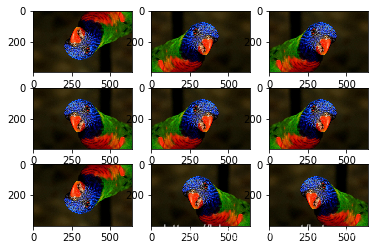
1.3 随机旋转
参数为最大旋转角度
# create image data augmentation generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=45)
# prepare iterator
it = datagen.flow(samples, batch_size=1)
# generate samples and plot
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# generate batch of images
batch = it.next()
# convert to unsigned integers for viewing
image = batch[0].astype('uint8')
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(image)
# show the figure
pyplot.show()
1.4 随机亮度变化
小于1.0表示变暗,大于1.0变亮,1.0不变
# create image data augmentation generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(brightness_range=[0.2,5.0])
# prepare iterator
it = datagen.flow(samples, batch_size=1)
# generate samples and plot
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# generate batch of images
batch = it.next()
# convert to unsigned integers for viewing
image = batch[0].astype('uint8')
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(image)
# show the figure
pyplot.show()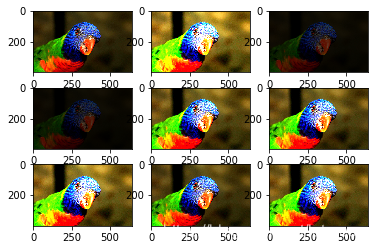
1.5 随机变焦
参数表示缩小,放大的最大范围
# create image data augmentation generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(zoom_range=[0.5,1.0])
# prepare iterator
it = datagen.flow(samples, batch_size=1)
# generate samples and plot
for i in range(9):
# define subplot
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
# generate batch of images
batch = it.next()
# convert to unsigned integers for viewing
image = batch[0].astype('uint8')
# plot raw pixel data
pyplot.imshow(image)
# show the figure
pyplot.show()
2 在实际训练场景中,数据增强技术的运用
1.图片来源于已知数据集,如mnist;
2.图片来源于普通图片,如本地的jpg,png等;
3.图片来源于panda数据集;
2.1 数据来源已知数据集,操作方法如下:
数据集已经全部读到内存中
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from matplotlib import pyplot
from keras import backend as K
#K.set_image_dim_ordering('th')
(train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = mnist.load_data()
train_data = train_data.reshape(train_data.shape[0], 1, 28, 28)
train_data = train_data.astype('float32')
# 创建图像生成器,指定对图像操作的内容,允许图片标准化处理
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(featurewise_center=True, featurewise_std_normalization=True, horizontal_flip=True)
# 图像生成器要训练的数据,计算均值,方差等
datagen.fit(train_data)
# 这是个图像生成迭代器,是可以无限生成各种新图片,这里指定每轮迭代只生成9张图片
for batch_data, batch_label in datagen.flow(train_data, train_label, batch_size=9):
for i in range(0, 9):
# 创建一个 3*3的九宫格,以显示图片
pyplot.subplot(330 + 1 + i)
pyplot.imshow(batch_data[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap=pyplot.get_cmap('gray'))
pyplot.show()
break
2.2数据来源图片集,其操作方法如下:
实际应用中,大部分场景是从硬盘读取图片,并且图片太多,不可能一次性都读到硬盘,那么可以对传入的目录,随机读取并且做数据增广
1.对已经读取到内存的单张图片数据(数组),做随机增广
可以为单个类别创建augment_times个增广图片
from numpy import expand_dims
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from matplotlib import pyplot
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from keras.preprocessing import image
import keras as K
# load the image
img = image.load_img('bird.jpg')
print(img)
# convert to numpy array
data_bird = image.img_to_array(img)
print(data_bird.shape)
pyplot.imshow(img)
data_gen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale = .1, # TODO:随机缩放图像RGB值的倍数
rotation_range =0.15 , # TODO:随机旋转图像的范围
zoom_range = 0.1, # TODO:随机缩放图像大小范围
width_shift_range = 0.2, # TODO:随机水平方向平移图像(fraction of total width)
height_shift_range= 0.2, # TODO:随机纵向平移图像(fraction of total height)
horizontal_flip=True,
)augment_times = 5
data_x = []
data_y = []
i = 0
for _ in range(augment_times):
face_aug = data_gen.random_transform(data_bird)
data_x.append(face_aug)
#data_y.append(name_dict[subdir])
plt.subplot(2,3,1+i)
plt.imshow(array_to_img(face_aug))#
i = i+1

2从目录随机读取所有类别图片,做数据增广
详细功能解释见代码注释
ps:实测发现迭代器产生图片的
#需要说明的是,这些增强图片都是在内存中实时批量迭代生成的,不是一次性被读入内存,这样可以极大地节约内存空间,加快处理速度。若想保留中间过程生成的增强图片,可以在上述方法中添加保存路径等参数,此处不再赘述。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
batch_size = 32
# 迭代50次
epochs = 50
# 依照模型规定,图片大小被设定为224
IMAGE_SIZE = 224
TRAIN_PATH = './data/17flowerclasses/train'
TEST_PATH = './data/17flowerclasses/test'
FLOWER_CLASSES = ['Bluebell', 'ButterCup', 'ColtsFoot']
# 使用数据增强
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=90)
# 可指定输出图片大小,因为深度学习要求训练图片大小保持一致
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(directory=TRAIN_PATH,
target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE),
classes=FLOWER_CLASSES)
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, array_to_img, img_to_array, load_img
import numpy as np
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest')
# 这里因为设置了save_to_dir参数,实际会保存所有增广图片到save_to_dir目录
dataflow_generator=datagen.flow_from_directory(r'./data/17flowerclasses/train',#类别子文件夹的上一级文件夹
batch_size=6,
shuffle=False,
save_to_dir=r'./train_result',
save_prefix='trans_',
save_format='jpg')
filenames = dataflow_generator.filenames
labels = dataflow_generator.class_indices
print(filenames)
#dataflow_generator实际上是一个无限迭代器
for i in range(1):
dataflow_generator.next()
sample_count = 10
i = 0
#此处image_data是一个2xlen(image_data[1])序列,
#image_data[0][...]存放batch_size张图片
#image_data[1][...]存放batch_size对应标签,默认自动创建为独热编码标签
for image_data in dataflow_generator:
print(len(image_data[1]))
for j in range(0,len(image_data[1])):
if i >= 15:
break
plt.subplot(3,5,1+i)
image = image_data[0][j].astype('uint8')
#print(type(image_data))
plt.imshow(array_to_img(image))#图片转化为image格式,方便显示
#plt.imshow(image)
i += 1
print(image_data[1][j]) #label
#print(image_data[0][0].shape) #image
sample_count -= 1
if sample_count <= 0:
breakFound 14 images belonging to 3 classes.
Found 14 images belonging to 3 classes.
['Bluebell/image_0241.jpg', 'Bluebell/image_0242.jpg', 'Bluebell/image_0243.jpg', 'Bluebell/image_0244.jpg', 'Bluebell/image_0245.jpg', 'ButterCup/image_1121.jpg', 'ButterCup/image_1122.jpg', 'ButterCup/image_1123.jpg', 'ButterCup/image_1124.jpg', 'ButterCup/image_1125.jpg', 'ColtsFoot/image_0881.jpg', 'ColtsFoot/image_0882.jpg', 'ColtsFoot/image_0883.jpg', 'ColtsFoot/image_0884.jpg']
6
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[0. 0. 1.]
2
[0. 0. 1.]
[0. 0. 1.]
6
[1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
6
[0. 1. 0.]
2
6
6
2
6
6
举一个从硬盘读取图片做数据增广多分类的实例
import csv
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
import sklearn
import os
import random
import tensorflow as tfBATCH_SIZE = 16
# 迭代50次
EPOCHS = 10
# 依照模型规定,图片大小被设定为224
IMAGE_SIZE = 224
TRAIN_PATH = './17flowerclasses/train'
TEST_PATH = './17flowerclasses/test'
FLOWER_CLASSES = ['Bluebell', 'ButterCup', 'ColtsFoot', 'Cowslip', 'Crocus', 'Daffodil', 'Daisy','Dandelion', 'Fritillary', 'Iris', 'LilyValley', 'Pansy', 'Snowdrop', 'Sunflower','Tigerlily', 'tulip', 'WindFlower']
# 使用数据增强
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest')
# 可指定输出图片大小,因为深度学习要求训练图片大小保持一致
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(directory=TRAIN_PATH,
target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE),
batch_size = BATCH_SIZE,
classes=FLOWER_CLASSES)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator()
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(directory=TEST_PATH,
target_size=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE),
classes=FLOWER_CLASSES)
Found 1190 images belonging to 17 classes.
Found 170 images belonging to 17 classes.from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, GlobalAveragePooling2D
from keras.layers import Dropout, Flatten, Dense
from keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential()
### TODO: 定义你的网络架构
model.add(Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=3, padding='valid', activation='relu', input_shape=(224, 224, 3)))
#model.add(Conv2D(32, (3,3), input_shape=(160, 160, 3), activation="relu"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2))
#model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=3, padding='valid', activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=3, padding='valid', activation='relu'))
model.add(GlobalAveragePooling2D())
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(17, activation='softmax'))
model.summary()Model: "sequential_18"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d_52 (Conv2D) (None, 222, 222, 32) 896
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_38 (MaxPooling (None, 111, 111, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_49 (Dropout) (None, 111, 111, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_53 (Conv2D) (None, 109, 109, 64) 18496
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_39 (MaxPooling (None, 54, 54, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_50 (Dropout) (None, 54, 54, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_54 (Conv2D) (None, 52, 52, 128) 73856
_________________________________________________________________
global_average_pooling2d_15 (None, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_51 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_21 (Dense) (None, 17) 2193
=================================================================
Total params: 95,441
Trainable params: 95,441
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint
# train the model
checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='flowers.weights.best.hdf5', verbose=1,
save_best_only=True)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])#model.fit(X_train,y_train,validation_split=0.2,shuffle=True,epochs=20)
history_object = model.fit_generator(train_generator,validation_data=test_generator, epochs=EPOCHS)Epoch 1/10
75/75 [==============================] - 29s 383ms/step - loss: 7.8649 - accuracy: 0.0849 - val_loss: 2.3924 - val_accuracy: 0.1176
Epoch 2/10
75/75 [==============================] - 28s 379ms/step - loss: 2.5159 - accuracy: 0.1689 - val_loss: 2.5512 - val_accuracy: 0.2471
Epoch 3/10
75/75 [==============================] - 28s 377ms/step - loss: 2.3332 - accuracy: 0.2563 - val_loss: 2.0680 - val_accuracy: 0.3000
Epoch 4/10
75/75 [==============================] - 28s 377ms/step - loss: 2.2113 - accuracy: 0.2866 - val_loss: 2.2407 - val_accuracy: 0.3059
Epoch 5/10
75/75 [==============================] - 28s 377ms/step - loss: 2.0356 - accuracy: 0.3244 - val_loss: 2.4963 - val_accuracy: 0.2941
Epoch 6/10
75/75 [==============================] - 29s 380ms/step - loss: 2.0376 - accuracy: 0.3403 - val_loss: 1.7107 - val_accuracy: 0.3588
Epoch 7/10
75/75 [==============================] - 30s 407ms/step - loss: 1.9415 - accuracy: 0.3689 - val_loss: 2.1597 - val_accuracy: 0.3118
Epoch 8/10
75/75 [==============================] - 32s 421ms/step - loss: 1.9102 - accuracy: 0.3571 - val_loss: 1.8596 - val_accuracy: 0.3353
Epoch 9/10
75/75 [==============================] - 31s 416ms/step - loss: 1.8563 - accuracy: 0.3975 - val_loss: 2.3684 - val_accuracy: 0.3235
Epoch 10/10
75/75 [==============================] - 31s 415ms/step - loss: 1.8305 - accuracy: 0.4202 - val_loss: 2.0994 - val_accuracy: 0.4118