梯度下降算法原理网上很多,我这里只是作为自己学习过程的札记,方便自己查看复习,因此不会那么详细,一般只记录对自己有用的部分。
1.什么是梯度?
可以简单理解为多变量函数的导数,即对每个变量单独求偏导。
梯度是改变率或者斜度的另一个称呼。如果你需要回顾这个概念,可以看下可汗学院对这个问题的讲解。
避免局部最低点方法:
https://ruder.io/optimizing-gradient-descent/index.html#momentum
可汗学院微积分:https://www.khanacademy.org/math/multivariable-calculus
矩阵:https://www.khanacademy.org/math/precalculus-2018/precalc-matrices
2.误差函数
首先,梯度下降法要求,误差函数是可微的,连续的;
这里用均方差(mean of the square errors,MSE)
$$
E = \frac{1}2m\sum_{\mu=1}^{m}(y^{\mu}-\hat{y}^\mu)^2
$$
3.梯度下降的基本过程:
误差函数就代表着一座山。我们的目标就是找到这个函数的最小值,也就是山底。
最快的下山的方式就是找到当前位置最陡峭的方向(梯度方向),然后沿着此方向向下走,因为梯度的方向就是函数之变化最快的方向;
重复这个过程,反复求取梯度,最后就能到达局部的最小值,这就类似于我们下山的过程。
4.实现基本函数
- Sigmoid 激活函数
$$\sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}$$
- 输出(预测)公式
$$\hat{y} = \sigma(w_1 x_1 + w_2 x_2 + b)$$
- 误差函数
$$Error(y, \hat{y}) = - y \log(\hat{y}) - (1-y) \log(1-\hat{y})$$
- 更新权重的函数
$$ w_i^{'} \longleftarrow w_i + \alpha (y - \hat{y}) x_i$$
$$ b^{'} \longleftarrow b + \alpha (y - \hat{y})$$
5.梯度计算公式推导
首先要注意的是 s 型函数具有很完美的导数。即
$$
\sigma'(x) = \sigma(x) (1-\sigma(x))
$$
原因是,我们可以使用商式计算它:

现在,如果有 m 个样本点,标为 $x^{(1)}, x^{(2)}, \ldots, x^{(m)}$
误差公式是:$E = -\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m \left( y^{(i)} \ln(\hat{y^{(i)}}) + (1-y^{(i)}) \ln (1-\hat{y^{(i)}}) \right)$
预测是: $\hat{y^{(i)}} = \sigma(Wx^{(i)} + b)$
我们的目标是计算E, 在单个样本点 x 时的梯度(偏导数),其中 x 包含 n 个特征,即 $x = (x_1, \ldots, x_n),$
$$
\nabla E =\left(\frac{\partial}{\partial w_1}E, \cdots, \frac{\partial}{\partial w_n}E, \frac{\partial}{\partial b}E \right)
$$
为此,首先我们要计算, $\frac{\partial}{\partial w_j} \hat{y}$
因为这是上述公式里的第一个元素,$\hat{y} = \sigma(Wx+b)$
因此:

最后一个等式是因为和中的唯一非常量项相对于 $w_j$ 正好是 $w_j x_j$, 明显具有导数 $x_j$.
现在可以计算 $\frac {\partial} {\partial w_j} E$

类似的计算将得出,针对单个样本点时,E 对 b 求偏导的公式为:
$$\frac {\partial} {\partial b} E=-(y -\hat{y})$$
这个实际上告诉了我们很重要的规则。对于具有坐标 $(x_1, \ldots, x_n)$ 的点,标签 y,预测$\hat{y}$, 该点的误差函数梯度是
$$ \left(-(y - \hat{y})x_1, \cdots, -(y - \hat{y})x_n, -(y - \hat{y}) \right) $$
总之
$$\nabla E(W,b) = -(y - \hat{y}) (x_1, \ldots, x_n, 1) $$
如果思考下,会发现很神奇。梯度实际上是标量乘以点的坐标!什么是标量?也就是标签和预测之间的差别。这意味着,如果标签与预测接近(表示点分类正确),该梯度将很小,如果标签与预测差别很大(表示点分类错误),那么此梯度将很大。
请记下:小的梯度表示我们将稍微修改下坐标,大的梯度表示我们将大幅度修改坐标。
如果觉得这听起来像感知器算法,其实并非偶然性!
6.梯度下降法更新权重的算法概述:
1.权重步长设定为 0: $\Delta w_i = 0$
2.对训练数据中的每一条记录:
a.通过网络做正向传播,计算输出 $\hat y = f(\sum_i w_i x_i)$
b.计算输出单元的误差项(error term) $\delta = (y - \hat y) * f'(\sum_i w_i x_i)$
c.更新权重步长 $\Delta w_i = \Delta w_i + \delta x_i$
d.更新权重 $w_i = w_i + \eta \Delta w_i / m$. 其中 $\eta$ 是学习率, m 是数据点个数。这里我们对权重步长做了平均,为的是降低训练数据中大的变化。
3.重复 e 代(epoch)。
你也可以对每条记录更新权重,而不是把所有记录都训练过之后再取平均。
7.梯度下降法实例
以一个二维平面点集的二分类为例,用梯度下降法拟合直线;
7.1读取与绘制数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#Some helper functions for plotting and drawing lines
def plot_points(X, y):
admitted = X[np.argwhere(y==1)]
rejected = X[np.argwhere(y==0)]
plt.scatter([s[0][0] for s in rejected], [s[0][1] for s in rejected], s = 25, color = 'blue', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.scatter([s[0][0] for s in admitted], [s[0][1] for s in admitted], s = 25, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
def display(m, b, color='g--'):
plt.xlim(-0.05,1.05)
plt.ylim(-0.05,1.05)
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
plt.plot(x, m*x+b, color)data = pd.read_csv('data.csv', header=None)
X = np.array(data[[0,1]])
y = np.array(data[2])
plot_points(X,y)
plt.show()
由上图可明显观测两个类别点集,用线性回归可以分类
# Implement the following functions
# Activation (sigmoid) function
# 激活函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# Output (prediction) formula
# 感知器输出
def output_formula(features, weights, bias):
return sigmoid(np.dot(features, weights) + bias)
# Error (log-loss) formula
# 误差函数
def error_formula(y, output):
return - y*np.log(output) - (1 - y) * np.log(1-output)
# Gradient descent step
# 用梯度更新权重
def update_weights(x, y, weights, bias, learnrate):
output = output_formula(x, weights, bias)
d_error = (y - output)
weights += learnrate * d_error * x
bias += learnrate * d_error
return weights, bias7.2 训练函数
该函数将帮助我们通过所有数据来迭代梯度下降算法,用于多个 epoch。 它还将绘制数据,以及在我们运行算法时绘制出一些边界线。
np.random.seed(44)
epochs = 100
learnrate = 0.01
def train(features, targets, epochs, learnrate, graph_lines=False):
errors = []
n_records, n_features = features.shape
last_loss = None
#获得随机值
weights = np.random.normal(scale=1 / n_features**.5, size=n_features)
bias = 0
for e in range(epochs):
del_w = np.zeros(weights.shape)
for x, y in zip(features, targets):
output = output_formula(x, weights, bias)
error = error_formula(y, output)
weights, bias = update_weights(x, y, weights, bias, learnrate)
# Printing out the log-loss error on the training set
out = output_formula(features, weights, bias)
loss = np.mean(error_formula(targets, out))
errors.append(loss)
if e % (epochs / 10) == 0:
print("\n========== Epoch", e,"==========")
if last_loss and last_loss < loss:
print("Train loss: ", loss, " WARNING - Loss Increasing")
else:
print("Train loss: ", loss)
last_loss = loss
predictions = out > 0.5
accuracy = np.mean(predictions == targets)
print("Accuracy: ", accuracy)
if graph_lines and e % (epochs / 100) == 0:
display(-weights[0]/weights[1], -bias/weights[1])
# Plotting the solution boundary
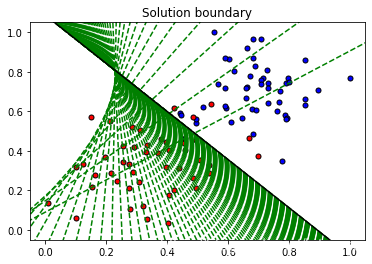
plt.title("Solution boundary")
display(-weights[0]/weights[1], -bias/weights[1], 'black')
# Plotting the data
plot_points(features, targets)
plt.show()
# Plotting the error
plt.title("Error Plot")
plt.xlabel('Number of epochs')
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.plot(errors)
plt.show()7.3训练算法
当我们运行该函数时,我们将获得以下内容:
- 目前的训练损失与准确性的 10 次更新
- 获取的数据图和一些边界线的图。 最后一个是黑色的。请注意,随着我们遍历更多的 epoch ,线会越来越接近最佳状态。
- 误差函数的图。 请留意,随着我们遍历更多的 epoch,它会如何降低。
train(X, y, epochs, learnrate, True)========== Epoch 0 ==========
Train loss: 0.7135845195381634
Accuracy: 0.4
========== Epoch 10 ==========
Train loss: 0.6225835210454962
Accuracy: 0.59
========== Epoch 20 ==========
Train loss: 0.5548744083669508
Accuracy: 0.74
========== Epoch 30 ==========
Train loss: 0.501606141872473
Accuracy: 0.84
========== Epoch 40 ==========
Train loss: 0.4593334641861401
Accuracy: 0.86
========== Epoch 50 ==========
Train loss: 0.42525543433469976
Accuracy: 0.93
========== Epoch 60 ==========
Train loss: 0.3973461571671399
Accuracy: 0.93
========== Epoch 70 ==========
Train loss: 0.3741469765239074
Accuracy: 0.93
========== Epoch 80 ==========
Train loss: 0.35459973368161973
Accuracy: 0.94
========== Epoch 90 ==========
Train loss: 0.3379273658879921
Accuracy: 0.94