首先是引导程序,即bootloader,简单说即bootloader会做如下事情:
(1)初始化物理内存;
(2)设置设备树;
(3)解压缩内核映像,将其加载到内核运行地址(可选);
(4)跳转到内核入口地址; 下面进入Linux范畴:
链接脚本vmlinux.lds.S
第一个要看的文件,“arch/arm64/kernel/vmlinux.lds.S”, Linux内核的链接脚本。
OUTPUT_ARCH(aarch64) ///编译目标文件格式为aarch64
ENTRY(_text) ///内核入口地址
Linux内核的内存布局定义
/***************************************************************************
* 内核的内存布局:
*
* 包括代码段(.text),只读数据段(.rodata),初始化数据段(.init.), .bss段等
* 几个常见的地址在arch/arm64/mm/init.c加了打印
*
**************************************************************************/
SECTIONS
{
. = KIMAGE_VADDR; ///内核的起始链接地址,
...
}
 查看vmlinux文件
查看vmlinux文件
aarch64-linux-gnu-readelf -S vmlinux
.head.text PROGBITS ffff800010000000 00010000
.text PROGBITS ffff800010010000 00020000
.rodata PROGBITS ffff8000107b0000 007c0000
.init.text PROGBITS ffff8000109a0000 009b0000
补充:用gdb单步调试内核时,启用MMU之前的代码,无法单步,究其原因,qemu默认的内存地址是0x40000000与链接脚本默认的KIMAGE_VADDR不一致,需要做一个重定位; 从以上vmlinux文件可知,几个重要段相对偏移是:
.head.text 0000
.text 10000
.rodata 7b0000
.init.text 9a0000
加上qemu运行物理内存地址0x40000000,加载vmlinux时,设置如下  导入vmlinux命令为:
导入vmlinux命令为:
add-symbol-file vmlinux 0x40010000 -s .head.text 0x40000000 -s .init.text 0x409a0000 -s .rodata 0x407b0000
设置PC值 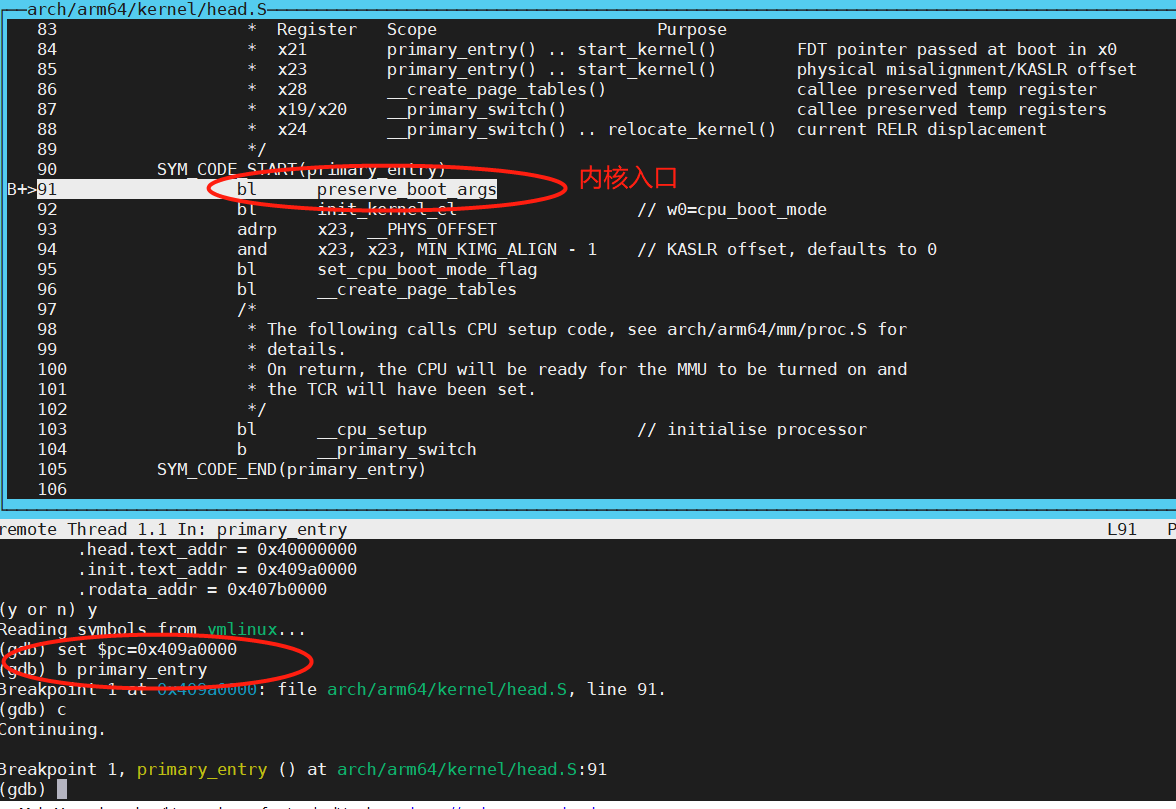 这样就可以对启用MMU之前的代码,正常设置断点,单步调试; ## 确认内核入口地址的方法
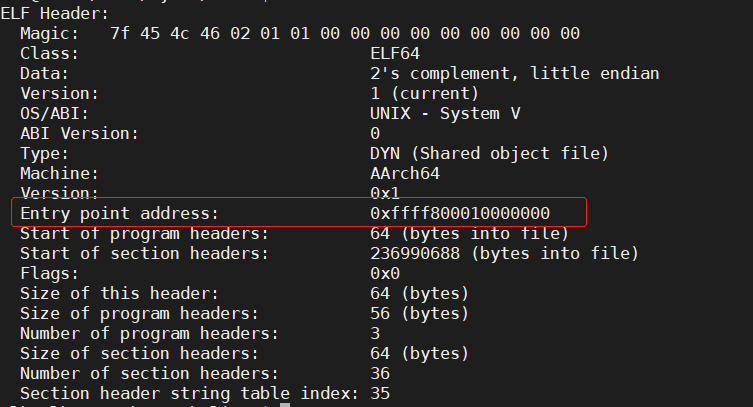
这样就可以对启用MMU之前的代码,正常设置断点,单步调试; ## 确认内核入口地址的方法
aarch64-linux-gnu-readelf -h vmlinux
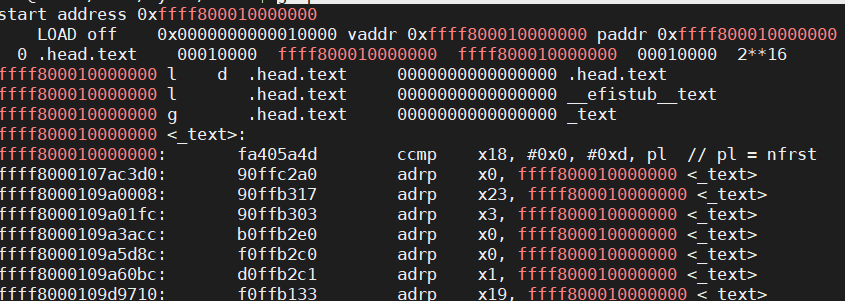
 反汇编vmlinux文件
反汇编vmlinux文件
aarch64-linux-gnu-objdump -dxh vmlinux > vmlinux.S
grep ffff800010000000 vmlinux.S
head.S文件
Bootload初始化完毕后,会跳转到内核入口处; 从head.S文件的
__INIT
#define __INIT .section .init.text,ax
可看出入口代码位于.init.text段,因此当设置PC值
set $pc=0x409a0000
pc指针跳到
SYM_CODE_START(primary_entry)
下面正式进入Linux单步运行环境; 首先,启动Linux对软硬件的需求如下:
/*
* Kernel startup entry point.
* ---------------------------
*
* The requirements are:
* MMU = off, D-cache = off, I-cache = on or off,
* x0 = physical address to the FDT blob.
*
* This code is mostly position independent so you call this at
* __pa(PAGE_OFFSET).
*
* Note that the callee-saved registers are used for storing variables
* that are useful before the MMU is enabled. The allocations are described
* in the entry routines.
*/
/*********************************************************************************
*
* ARMV8支持EL2和EL3,这些异常等级都可以引导Linux内核的运行;
* Linux内核运行在EL1,
* kernel启动条件的要求:
* CPU:
* 屏蔽CPU上所有的中断,比如清除PSTATE寄存器的DAIF域;
* CPU必须处在EL2或非安全模式的EL1
*
* MMU和高速缓存:
* 关闭MMU;
* 关闭数据高速缓存;//清除内核镜像加载的地址范围的高速缓存,最简单办法,关闭缓存
* 指令高速缓存可关闭或打开;//因为u-boot和内核指令代码不会重叠,缓存不会出错
*
* 其他:
* X0寄存器指向设备树的物理地址;
* 设置时钟,CNTFRQ和CNTVOFF寄存器;
* 内存一致性;
*
* U-boot的作用是加载内核镜像到内存,跳转到kernel入口地址,即这里!
********************************************************************************/
__HEAD
/*
* DO NOT MODIFY. Image header expected by Linux boot-loaders.
*/
efi_signature_nop // special NOP to identity as PE/COFF executable
b primary_entry // branch to kernel start, magic ///跳转到内核启动汇编代码入口
进入Linux内核,汇编部分主要完成以下工作:
SYM_CODE_START(primary_entry)
bl preserve_boot_args ///保持启动参数到boot_args[]数组
bl init_kernel_el // w0=cpu_boot_mode ///切换到EL1模式,已运行kernel
adrp x23, __PHYS_OFFSET
and x23, x23, MIN_KIMG_ALIGN - 1 // KASLR offset, defaults to 0
bl set_cpu_boot_mode_flag ///设置set_cpu_boot_mode_flag全局变量
bl __create_page_tables ///创建恒等映射页表,以及内核映像映射页表
/*
* The following calls CPU setup code, see arch/arm64/mm/proc.S for
* details.
* On return, the CPU will be ready for the MMU to be turned on and
* the TCR will have been set.
*/
bl __cpu_setup // initialise processor ///为打开MMU做一些处理器相关的初始化
b __primary_switch ///启动MMU,并跳转到start_kernel()函数(进入内核的C语言部分)
SYM_CODE_END(primary_entry)
下面细看每个函数内容 # preserve_boot_args()函数
/*
* Preserve the arguments passed by the bootloader in x0 .. x3
*/
///把引导程序传递过来的参数x0~x3保存到boot_args[]数组中
SYM_CODE_START_LOCAL(preserve_boot_args)
mov x21, x0 // x21=FDT,x0设备树地址,暂存在x21
adr_l x0, boot_args // record the contents of
stp x21, x1, [x0] // x0 .. x3 at kernel entry
stp x2, x3, [x0, #16] ///4个参数存入boot_args
dmb sy // needed before dc ivac with
// MMU off
///保证后面__inval_dcache_area清除缓存前,执行完stp指令,保证参数保存完整性
mov x1, #0x20 // 4 x 8 bytes
///x0为设备树地址,x1=32为长度,__inval_dcache_area使boot_args[]数组对应的高速缓存失效,并清除缓存
b __inval_dcache_area // tail call
SYM_CODE_END(preserve_boot_args)
init_kernel_el函数
设置ARM64运行等级
SYM_FUNC_START(init_kernel_el)
mrs x0, CurrentEL
cmp x0, #CurrentEL_EL2
b.eq init_el2
SYM_INNER_LABEL(init_el1, SYM_L_LOCAL)
mov_q x0, INIT_SCTLR_EL1_MMU_OFF ///设置大小端
msr sctlr_el1, x0
isb ///刷新流水线
mov_q x0, INIT_PSTATE_EL1 ///屏蔽外部中断信号
msr spsr_el1, x0
msr elr_el1, lr ///设置el1返回地址
mov w0, #BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL1 ///返回值,ARM64当前运行等级el1
eret
SYM_INNER_LABEL(init_el2, SYM_L_LOCAL)set_cpu_boot_mode_flag
/*
* Sets the __boot_cpu_mode flag depending on the CPU boot mode passed
* in w0. See arch/arm64/include/asm/virt.h for more info.
*/
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(set_cpu_boot_mode_flag)
adr_l x1, __boot_cpu_mode ///全局变量,存放本地CPU执行等级
cmp w0, #BOOT_CPU_MODE_EL2
b.ne 1f
add x1, x1, #4 ///EL2,存放在__boot_cpu_mode[1]
1: str w0, [x1] // This CPU has booted in EL1 ///w0为init_kernel_el函数返回的当前CPU异常等级
dmb sy ///确保__boot_cpu_mode数据完整刷回内存;
dc ivac, x1 // Invalidate potentially stale cache line
ret
SYM_FUNC_END(set_cpu_boot_mode_flag)
__create_page_tables
///创建恒等映射页表,以及内核映像映射页表
恒等映射
(1)CPU启动时,MMU是关闭的,CPU访问的是物理地址,而MMU开启后,访问的是虚拟地址;
(2)现代处理器大多支持多级流水线,处理器会提前预取多条指令到流水线中,当打开MMU时,CPU已经预取多条指令到流水线中,并且这些指令都是用物理地址预取的; MMU开启后,将以虚拟地址访问,这样继续访问流水线中预取的指令(按物理地址预取),就很容易出错; 为解决这个问题,引入“恒等映射”,即将虚拟地址映射到相等的物理地址,可以巧妙的解决上述问题; 这里建立的恒等映射是小范围的,一般内核镜像占用的空间就几M; 恒等映射完毕,开启MMU,CPU进入虚拟地址访问阶段;
/*
* 在vmlinux.lds.S定义,大小为IDMAP_DIR_SIZE,通常为3个连续4KB页面,分别对应PGD,PUD和PMD页表
* 这里要建立一个2MB大小的块映射
* idmap_pg_dir = .;
* . += IDMAP_DIR_SIZE;
* idmap_pg_end = .;
*/
adrp x0, idmap_pg_dir
///.idmap.text段的起始地址,除了开机启动时打开MMU外,内核还有许多场景需要恒等映射,如唤醒处理器的函数cpu_do_resume
adrp x3, __idmap_text_start // __pa(__idmap_text_start)
...
mov x5, #VA_BITS_MIN ///这里配置为48bit
1:
adr_l x6, vabits_actual
str x5, [x6] ///VA_BITS_MIN的值保存在全局变量vabits_actual中
dmb sy //保证str指令数据刷新到内存
dc ivac, x6 // Invalidate potentially stale cache line
/*
* VA_BITS may be too small to allow for an ID mapping to be created
* that covers system RAM if that is located sufficiently high in the
* physical address space. So for the ID map, use an extended virtual
* range in that case, and configure an additional translation level
* if needed.
*
* Calculate the maximum allowed value for TCR_EL1.T0SZ so that the
* entire ID map region can be mapped. As T0SZ == (64 - #bits used),
* this number conveniently equals the number of leading zeroes in
* the physical address of __idmap_text_end.
*/
adrp x5, __idmap_text_end
clz x5, x5 ///统计x5第一个1前由多少个0
cmp x5, TCR_T0SZ(VA_BITS_MIN) // default T0SZ small enough?
b.ge 1f // .. then skip VA range extension ///__idmap_text_end没超过VA_BITS_MIN表达的范围,跳转1f
adr_l x6, idmap_t0sz
str x5, [x6]
dmb sy
dc ivac, x6 // Invalidate potentially stale cache line
...
1:
ldr_l x4, idmap_ptrs_per_pgd //idmap_ptrs_per_pgd等于PTRS_PER_PGD,表示PGD页表由多少个页表项
mov x5, x3 // __pa(__idmap_text_start)
adr_l x6, __idmap_text_end // __pa(__idmap_text_end)
///调用map_memory宏建立__idmap_text代码段 的映射页表;
/*
* x0:idmap_pg_dir
* x1:
* x3:__idmap_text_start
* x6: __idmap_text_end
* x7: SWAPPER_MM_MMUFLAGS
* x3: __idmap_text_start
* x4: PTRS_PER_PGD
*/
map_memory x0, x1, x3, x6, x7, x3, x4, x10, x11, x12, x13, x14
map_memory宏分析
/* tbl:页表起始地址,页表基地址
* rtbl:下一级页表起始地址,通常是tbl+PAGE_SIZE
* vstart:要映射的虚拟地址的起始地址
* vend:要映射的虚拟地址的结束地址
* flags:最后一级页表的属性
* phys:映射的物理地址
* pgds:PGD页表项的个数
*/
.macro map_memory, tbl, rtbl, vstart, vend, flags, phys, pgds, istart, iend, tmp, count, sv
add \rtbl, \tbl, #PAGE_SIZE
mov \sv, \rtbl
mov \count, #0
///compute_indices宏计算vstart,vend在页表中的索引值
compute_indices \vstart, \vend, #PGDIR_SHIFT, \pgds, \istart, \iend, \count
///设置页表内容,分别填充一级页表PGD,二级页表PMD, 最后一级页表PT
populate_entries \tbl, \rtbl, \istart, \iend, #PMD_TYPE_TABLE, #PAGE_SIZE, \tmp
mov \tbl, \sv
mov \sv, \rtbl
#if SWAPPER_PGTABLE_LEVELS > 3
compute_indices \vstart, \vend, #PUD_SHIFT, #PTRS_PER_PUD, \istart, \iend, \count
populate_entries \tbl, \rtbl, \istart, \iend, #PMD_TYPE_TABLE, #PAGE_SIZE, \tmp
mov \tbl, \sv
mov \sv, \rtbl
#endif
#if SWAPPER_PGTABLE_LEVELS > 2
compute_indices \vstart, \vend, #SWAPPER_TABLE_SHIFT, #PTRS_PER_PMD, \istart, \iend, \count
populate_entries \tbl, \rtbl, \istart, \iend, #PMD_TYPE_TABLE, #PAGE_SIZE, \tmp
mov \tbl, \sv
#endif
compute_indices \vstart, \vend, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SHIFT, #PTRS_PER_PTE, \istart, \iend, \count
bic \count, \phys, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE - 1
populate_entries \tbl, \count, \istart, \iend, \flags, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE, \tmp
.endm
compute_indices 宏
/**************************************************************
* func:计算vstart,vend在页表的索引值,返回值填在istart,iend
*
* vstart:虚拟地址的起始地址
* vend:虚拟地址结束地址;
* shift各级页表在虚拟地址中的偏移;
* ptrs:页表项的个数;
* istart:vstart索引值;
* iend:vend索引值;
* count
**************************************************************/
.macro compute_indices, vstart, vend, shift, ptrs, istart, iend, count
lsr \iend, \vend, \shift
mov \istart, \ptrs
sub \istart, \istart, #1
and \iend, \iend, \istart // iend = (vend >> shift) & (ptrs - 1) iend索引值
mov \istart, \ptrs
mul \istart, \istart, \count
add \iend, \iend, \istart // iend += (count - 1) * ptrs
// our entries span multiple tables
//跨多个表
lsr \istart, \vstart, \shift
mov \count, \ptrs
sub \count, \count, #1
and \istart, \istart, \count ///istart索引值istart = (vstart >> shift) & (ptrs - 1)
sub \count, \iend, \istart ///页表项个数
.endm
populate_entries宏
/*******************************************************************
* 填写页表
*
* tbl: 页表基地址
* rtbl: 下级页表基地址
* index: 写入页表的起始索引
* eindex: 页表结束索引
* flags: 页表属性
* inc:
* tmp1: temporary variable
*********************************************************************/
.macro populate_entries, tbl, rtbl, index, eindex, flags, inc, tmp1
.Lpe\@: phys_to_pte \tmp1, \rtbl
orr \tmp1, \tmp1, \flags // tmp1 = table entry
str \tmp1, [\tbl, \index, lsl #3] ///
add \rtbl, \rtbl, \inc // rtbl = pa next level ///这里我理解为rtbl的下一个页(简单理解为相邻下个物理页),而不是下一级,跟注释有点不同?
add \index, \index, #1
cmp \index, \eindex ///判断是否填充完,未完则继续填写下一个
b.ls .Lpe\@
.endm
综上,.idmap.text段的虚拟地址映射到了相同的物理地址上,这个映射表在idmap_pg_dir中;
问题:那些函数在这个映射的2MB内存中?
由head.s中的定义知
.section .idmap.text,awx
__enable_mmu, __primary_switch, __cput_setup等汇编函数都在.idmap.text段中; 可以从System.map文件中得到验证; 这些函数在Linux“自举”过程中会用到;
粗粒度的内核镜像映射
问题:为什么要创建第二个页表?
CPU刚启动时,物理内存一般都在低地址(不会超过256T大小),恒等映射的地址实际在用户空间了,即MMU启用后idmap_pg_dir会填入TTBR0; 而内核空间的链接地址都是在高地址(内核空间在高地址),需要填入TTBR1; 因此,这里再建一张表,映射整个内核镜像,且虚拟地址空间是在高地址区0xffffxxxx xxxx xxxx
/*
* Map the kernel image (starting with PHYS_OFFSET).
*/
///调用map_memory宏建立整个内核镜像代码段 的映射页表;
/**************************************************************************
* 为什么要建第二张表?
* CPU刚启动时,物理内存一般都在低地址(不会超过256T大小),恒等映射的地址实际在用户空间了,
* 即MMU启用后idmap_pg_dir会填入TTBR0;
* 而内核空间的链接地址都是在高地址(内核空间在高地址),需要填入TTBR1;
* 因此,这里再建一张表,映射整个内核镜像,且虚拟地址空间是在高地址区0xffffxxxx xxxx xxxx
* 注:init_pg_dir和idmap_pg_dir两个页表映射区别:
* (1)init_pg_dir映射的虚拟地址在高位0xffff xxxx xxxx xxxx;
* idmap_pg_dir映射的虚拟地址在低位0x0000 xxxx xxxx xxxx;
* MMU启用后,init_pg_dir填入TTBR1,idmap_pg_dir填入TTBR0;
* (2)init_pg_dir映射大小是整个内核镜像,idmap_pg_dir映射2M, 只是内存访问过渡,成功开启MMU即可;
***************************************************************************/
adrp x0, init_pg_dir
mov_q x5, KIMAGE_VADDR // compile time __va(_text)
add x5, x5, x23 // add KASLR displacement
mov x4, PTRS_PER_PGD
adrp x6, _end // runtime __pa(_end)
adrp x3, _text // runtime __pa(_text)
sub x6, x6, x3 // _end - _text
add x6, x6, x5 // runtime __va(_end)
map_memory x0, x1, x5, x6, x7, x3, x4, x10, x11, x12, x13, x14
__cpu_setup函数
// initialise processor ///为打开MMU做一些处理器相关的初始化
/*
* __cpu_setup
*
* Initialise the processor for turning the MMU on.
*
* Output:
* Return in x0 the value of the SCTLR_EL1 register.
*/
.pushsection .idmap.text, awx ///把__cpu_setup连接到.idmap.text段
SYM_FUNC_START(__cpu_setup)
tlbi vmalle1 // Invalidate local TLB ///本地TLB无效
dsb nsh ///确保tlbi执行完
mov x1, #3 << 20
msr cpacr_el1, x1 // Enable FP/ASIMD ///设定EL0,EL1可以访问浮点单元,SIMD单元
mov x1, #1 << 12 // Reset mdscr_el1 and disable
msr mdscr_el1, x1 // access to the DCC from EL0
isb // Unmask debug exceptions now,
enable_dbg // since this is per-cpu ///打开PSATE调试功能
reset_pmuserenr_el0 x1 // Disable PMU access from EL0
reset_amuserenr_el0 x1 // Disable AMU access from EL0
/*
* Default values for VMSA control registers. These will be adjusted
* below depending on detected CPU features.
*/
mair .req x17
tcr .req x16
mov_q mair, MAIR_EL1_SET
///设置TCR寄存器,TCR用于管理页表映射
mov_q tcr, TCR_TxSZ(VA_BITS) | TCR_CACHE_FLAGS | TCR_SMP_FLAGS | \
TCR_TG_FLAGS | TCR_KASLR_FLAGS | TCR_ASID16 | \
TCR_TBI0 | TCR_A1 | TCR_KASAN_SW_FLAGS
...
tcr_clear_errata_bits tcr, x9, x5
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_VA_BITS_52
ldr_l x9, vabits_actual
sub x9, xzr, x9
add x9, x9, #64
tcr_set_t1sz tcr, x9
#else
ldr_l x9, idmap_t0sz
#endif
tcr_set_t0sz tcr, x9
/*
* Set the IPS bits in TCR_EL1.
*/
tcr_compute_pa_size tcr, #TCR_IPS_SHIFT, x5, x6 ///IPS域,设置位宽
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_HW_AFDBM
/*
* Enable hardware update of the Access Flags bit.
* Hardware dirty bit management is enabled later,
* via capabilities.
*/
mrs x9, ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1
and x9, x9, #0xf
cbz x9, 1f
orr tcr, tcr, #TCR_HA // hardware Access flag update
1:
#endif /* CONFIG_ARM64_HW_AFDBM */
msr mair_el1, mair
msr tcr_el1, tcr
/*
* Prepare SCTLR
*/
mov_q x0, INIT_SCTLR_EL1_MMU_ON ///返回值,下个函数__enable_mmu的参数
ret // return to head.S
.unreq mair
.unreq tcr
SYM_FUNC_END(__cpu_setup)
__primary_switch函数
///启动MMU,并跳转到start_kernel()函数(进入内核的C语言部分)
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(__primary_switch)
#ifdef CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE ///内核启动时对内核映像的虚拟地址重新映射,防止黑客攻击
mov x19, x0 // preserve new SCTLR_EL1 value
mrs x20, sctlr_el1 // preserve old SCTLR_EL1 value
#endif
adrp x1, init_pg_dir
bl __enable_mmu ///参数x0->SCTLR_EL1,x1->init_pg_dir页表基地址,开启MMU
#ifdef CONFIG_RELOCATABLE ///配置重新映射内核镜像
#ifdef CONFIG_RELR
mov x24, #0 // no RELR displacement yet
#endif
bl __relocate_kernel
#ifdef CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE
ldr x8, =__primary_switched
adrp x0, __PHYS_OFFSET
blr x8
/*
* If we return here, we have a KASLR displacement in x23 which we need
* to take into account by discarding the current kernel mapping and
* creating a new one.
*/
pre_disable_mmu_workaround
msr sctlr_el1, x20 // disable the MMU
isb
bl __create_page_tables // recreate kernel mapping
tlbi vmalle1 // Remove any stale TLB entries
dsb nsh
isb
set_sctlr_el1 x19 // re-enable the MMU
bl __relocate_kernel
#endif
#endif
ldr x8, =__primary_switched
adrp x0, __PHYS_OFFSET
br x8 ///实现重映射
SYM_FUNC_END(__primary_switch)
__enable_mmu函数
/*
* Enable the MMU.
*
* x0 = SCTLR_EL1 value for turning on the MMU.
* x1 = TTBR1_EL1 value
*
* Returns to the caller via x30/lr. This requires the caller to be covered
* by the .idmap.text section.
*
* Checks if the selected granule size is supported by the CPU.
* If it isn't, park the CPU
*/
SYM_FUNC_START(__enable_mmu)
mrs x2, ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1
ubfx x2, x2, #ID_AA64MMFR0_TGRAN_SHIFT, 4
cmp x2, #ID_AA64MMFR0_TGRAN_SUPPORTED_MIN
b.lt __no_granule_support
cmp x2, #ID_AA64MMFR0_TGRAN_SUPPORTED_MAX
b.gt __no_granule_support
update_early_cpu_boot_status 0, x2, x3
adrp x2, idmap_pg_dir
phys_to_ttbr x1, x1
phys_to_ttbr x2, x2
msr ttbr0_el1, x2 // load TTBR0
offset_ttbr1 x1, x3
msr ttbr1_el1, x1 // load TTBR1 //填充两个页表基地址到TTBR0,TTBR1
isb
set_sctlr_el1 x0 //填充M域,使能MMU
ret
SYM_FUNC_END(__enable_mmu)
__primary_switched函数
/*
* The following fragment of code is executed with the MMU enabled.
*
* x0 = __PHYS_OFFSET
*/
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(__primary_switched)
adrp x4, init_thread_union ///init_thread_union指向thread_union数据结构,其中包含系统第一个进程(init进程)的内核栈
add sp, x4, #THREAD_SIZE ///sp指向栈顶
adr_l x5, init_task
msr sp_el0, x5 // Save thread_info ///sp_el0在EL1模式下无效,这里用来存init进程的task_struct指针是合适的
adr_l x8, vectors // load VBAR_EL1 with virtual
msr vbar_el1, x8 // vector table address ///填充异常向量表地址
isb ///确保以上指令执行完
stp xzr, x30, [sp, #-16]!
mov x29, sp ///sp存放到x29
#ifdef CONFIG_SHADOW_CALL_STACK
adr_l scs_sp, init_shadow_call_stack // Set shadow call stack
#endif
str_l x21, __fdt_pointer, x5 // Save FDT pointer ///保存设备树的地址
ldr_l x4, kimage_vaddr // Save the offset between
sub x4, x4, x0 // the kernel virtual and
str_l x4, kimage_voffset, x5 // physical mappings
// Clear BSS
///清除未初始化的数据段
adr_l x0, __bss_start
mov x1, xzr
adr_l x2, __bss_stop
sub x2, x2, x0
bl __pi_memset
dsb ishst // Make zero page visible to PTW
...
bl switch_to_vhe // Prefer VHE if possible
add sp, sp, #16
mov x29, #0
mov x30, #0 //sp指向内核栈顶
b start_kernel //跳转到C语言入口
SYM_FUNC_END(__primary_switched)